Figure 3. Au(CN)2− block of R334C is relatively independent of the extracellular anion.
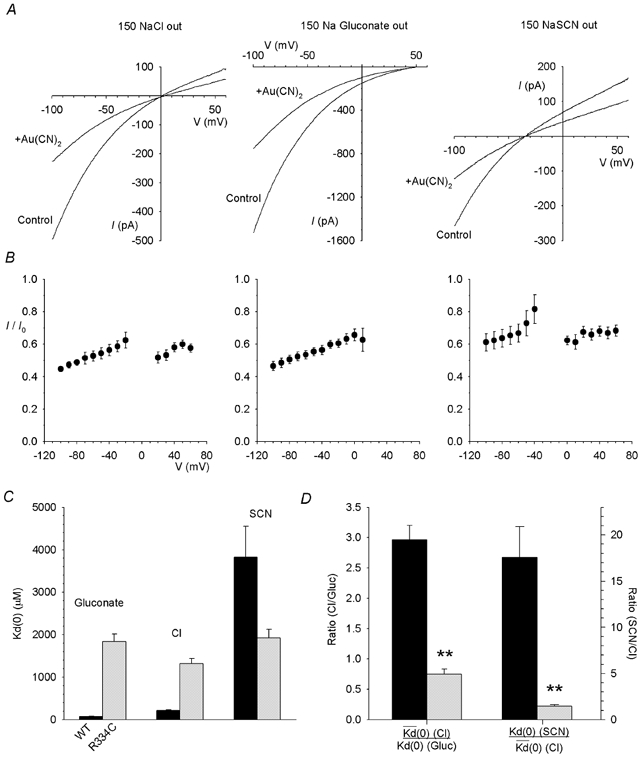
A, example R334C-CFTR I-V relationships recorded before (control) and after (+Au(CN)2) addition of 1 mm Au(CN)2− to the intracellular solution, with 150 mm NaCl, sodium gluconate or NaSCN present in the extracellular solution. B, mean fraction of control current remaining (I/I0) following addition of 1 mm Au(CN)2− for the same ionic conditions as shown in A. C, Kd(0) is strongly affected by the extracellular anion in wild-type (black bars) but not in R334C (grey bars). D, the effect of changing the extracellular anion (from Cl− to gluconate or from Cl− to SCN−) on the strength of Au(CN)2− block, as quantified by the ratio of Kd(0) values estimated under different ionic conditions as described in Methods, is significantly reduced in R334C (grey bars) relative to wild-type (black bars) (**P < 0.001). Mean of data from 5 patches in each case.
