Figure 1. Effect of nitrergic nerve stimulation on the frequency and amplitude of unitary potentials in the circular layer of guinea-pig gastric antrum.
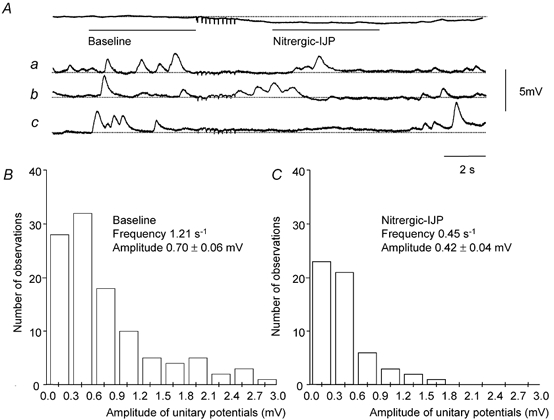
A, a train of stimuli (10 impulses at 5 Hz) evoked a nitrergic-IJP with a peak amplitude of 0.7 mV. A sample of three (traces a-c) of the 35 individual traces which made up this averaged response is shown below. The rate of occurrence of unitary potentials fell during the nitrergic-IJP from 1.21 to 0.45 s−1. The amplitude frequency histograms of unitary potentials, determined from the baseline period (B) and during the nitrergic-IJP (C), showed that the mean amplitude of the unitary potentials fell from 0.7 to 0.42 mV. The resting membrane potential was −61 mV(Aa-c); in preparations where the frequency of unitary potentials was low this corresponded with the peak hyperpolarization detected during the nitrergic-IJP. Time and voltage calibration bars apply to all recordings. Nifedipine (1 μM), atropine (1 μM) and apamin (0.1 μM) were present throughout.
