Figure 9. Effect of acidosis on the csNSC channel-mediated membrane depolarization and the excitation of hippocampal neurons.
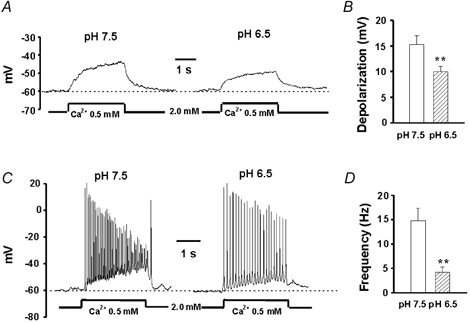
A, representative traces showing membrane depolarization in the presence of TTX (0.5 μM) by lowering [Ca2+]o from 2.0 to 0.5 mM at pH 7.5 and 6.5. B, summary data from 7 neurons showing the effect of acidosis on the amplitude of membrane depolarization induced by lowering [Ca2+]o. The amplitude of membrane depolarization induced by lowering [Ca2+]o to 0.5 mM was 15.3 ± 1.7 mV at pH 7.5 and 9.9 ± 1.0 mV at pH 6.5 (n = 6, P < 0.01). C, representative traces showing membrane depolarization and excitation of a hippocampal neuron by lowering [Ca2+]o from 2.0 to 0.5 mM at pH 7.5 or 6.5. D, summary data from 8 neurons showing the frequency of action potential firing at pH 7.5 and 6.5. The frequency of action potential firing in the presence of 0.5 mM [Ca2+]o was 14.8 ± 2.6 Hz at pH 7.5 and 4.3 ± 1.1 Hz at pH 6.5 (n = 8, P < 0.01). All solutions contained 1 mM Mg2+. ** P < 0.01 compared with the pH 7.5 group.
