Figure 3. Inactivity decreases both muscle TG uptake and plasma HDL-C.
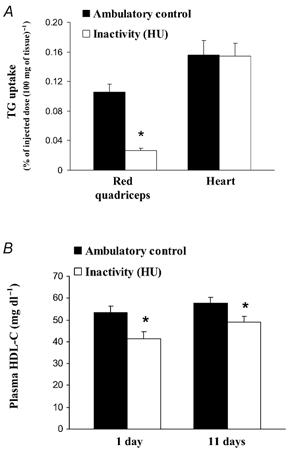
The accumulation of TG-derived fatty acids in the RQ hindlimb muscles and heart (n = 3) was determined 10 min after injection of [3H]triolein-labelled chylomicron-like emulsion in rats following 18 h of HU and compared with rats with normal ambulatory activity (A). Rats with both 1 day (n = 6) and 11 days (n = 8) of intermittent (10–12 h HU day−1) inactivity had a significantly lower plasma HDL-C concentration compared with active controls (B). *P < 0.05 between HU and low-intensity ambulatory control.
