Figure 1. The effects of 8-Bromo-cGMP (Br-cGMP) on the ciliary beat frequency (CBF) and [Ca2+]i of rabbit airway ciliated cells.
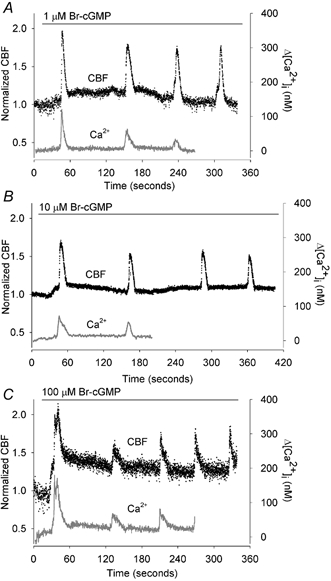
Data for both CBF and [Ca2+]i are normalized with the initial basal value and are representative of multiple cells. A, 1 μM Br-cGMP induced a two-part response in the CBF consisting of a small increase in the basal CBF (basal CBF = 10.4 Hz) that reached a maximum level within 60 s and declined thereafter, and larger transient increases in CBF that were superimposed on the basal CBF. By contrast, Br-cGMP only induced a series of transient increases in the [Ca2+]i without affecting the basal [Ca2+]i (n = 10). B, 10 μM Br-cGMP induced a higher sustained increase in the basal CBF (basal CBF = 15.9 Hz) but the superimposed transient increases in CBF, as well as the transient increases in [Ca2+]i, were unchanged (n = 11). C, 100 μM Br-cGMP only induced a further increase in the sustained CBF increase (basal CBF = 14.1 Hz) (n = 11). A-C, in all cases, the sustained increases in CBF occurred in the absence of changes in [Ca2+]i while the transient changes in CBF and [Ca2+]i were tightly coupled.
