Figure 6. Effects of ZD7288 on the generation of action potentials.
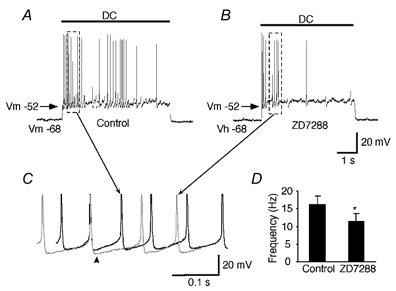
Repetitive action potentials generated by artificial membrane depolarization using DC current injection before (A) and after (B) the bath application of ZD7288 (100 μm). The intensity of the injected DC current was adjusted to produce the same depolarized membrane potential (e.g. holding potential, Vh =−52 mV). ZD7288-induced hyperpolarization was compensated by continuous DC current injection to hold the membrane potential at the value of the initial resting level (e.g. −68 mV). C, enlargements of the portion indicated by the dashed rectangle in A and B. Traces were superimposed according to their firing threshold. Note an increase in the AHP amplitude and the prolonged time course of the AHP phase (arrowhead). D, mean values for the frequency of action potentials before and during the application of ZD7288 (* P < 0.01, n = 5).
