Figure 3. Overview brain region proliferation.
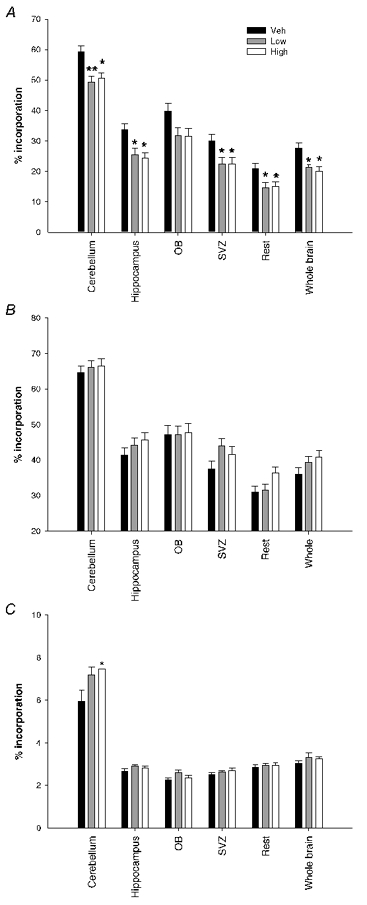
Graph showing the effect of prenatal betamethasone on postnatal brain region proliferation in both males and females combined. Betamethasone treatment caused significant decreases in proliferation at P1 in all brain regions (dose effect P < 0.05)except for the olfactory bulb (A). B, by P2 this effect is reversed with no significant differences overall but with clear sex effects. At P2 the males showed significantly increased brain cell proliferation whereas the female brain continued to have inhibited proliferation due to the treatment. C, at P21 the cerebellum is still proliferating at increased levels due to the prenatal betamethasone treatment (cerebellum overall dose effect P = 0.024). Values represent means ± s.e.m., n = 12–16 per dose per time; * P < 0.05 compared to vehicle, ** P < 0.001 compared to vehicle.
