Figure 2. Effects of intracerebroventricular administration of the cholinergic antagonist methscopolamine on pancreatic secretion in conscious rats.
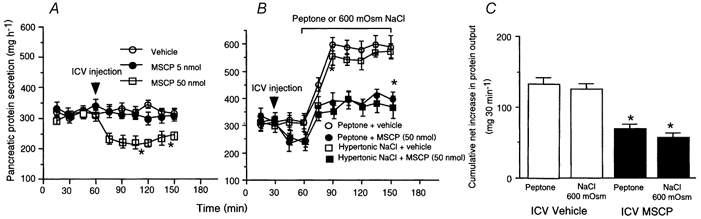
A, intracerebroventricular (I.C.V.) administration of methscopolamine (MSCP) at a dose of 5 nmol had no effect on basal pancreatic protein output, whereas a 50-nmol dose induced a decrease in basal pancreatic protein output from 320to 210 mg h−1. B, intraduodenal infusion of peptone and hypertonic NaCl increased protein secretion by 100 % and 70 %, respectively. We have previously shown that these responses are mediated by a vagal mucosal afferent pathway. I.C.V. MSCP administration partially inhibited pancreatic protein output stimulated by peptone or hypertonic NaCl. C, cumulative net increase in pancreatic protein output in response to intraluminal peptone or hypertonic NaCl was significantly reduced in decerebrate rats compared to controls. Values are means ± S.E.M. for 4 rats in each group. *P < 0.05 compared with sham operation.
