Figure 10. Effects of lateral or medial parabrachial nucleus lesions induced by ibotenic acid on pancreatic secretion in conscious rats.
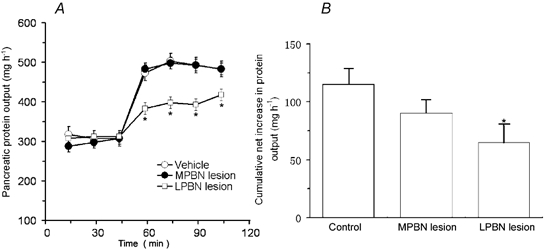
A, time course of peptone-stimulated pancreatic secretion in control rats and in rats with lateral parabrachial nucleus (LPBN) or medial PBN (MPBN) lesions. B, cumulative net increases in protein output stimulated by peptone. Ibotenic acid treatment had no effect on basal pancreatic secretion. Lateral parabrachial nucleus (LPBN) lesion significantly reduced pancreatic protein secretion in response to intraduodenal perfusion of peptone, suggesting that LPBN neurons are involved in mediating pancreatic secretion evoked by the vago-vagal reflex. Values are means ± S.E.M. for 4 rats with MPBN lesion and 5 rats with LPBN lesion. *P < 0.05 compared with basal in A and with control in B.
