Figure 3. Co-immunoprecipitation of mSlo or bSlo BKCa channels with syntaxin 1A following transient co-expression in HEK 293 cells.
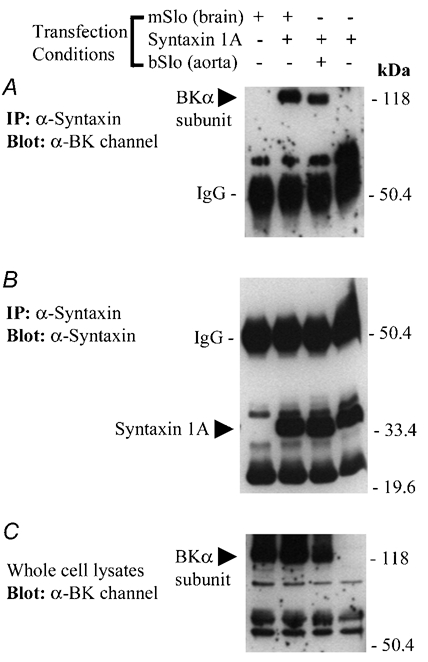
A, Western blot of solubilized protein material immunoprecipitated from four groups of transfected HEK 293 cells using the anti-syntaxin 1A monoclonal antibody, HPC-1. The absence (−) or presence (+) of BKCa channel or syntaxin 1A cDNA in the transfection medium for each group of cells is indicated above the panel. The blot has been probed with a polyclonal antibody (Chemicon) recognizing the BKCa channel α subunit. The positions of the mouse brain and bovine aortic BKCa channel α subunits and the IgG heavy chain are indicated on the left-hand side of the blot. Following immunodetection of the BKCa channel, the same nitrocellulose membrane shown in A was stripped and then re-probed for the presence of syntaxin 1A, using the monoclonal antibody HPC-1 (B). The positions of the syntaxin 1A monomer and the IgG heavy chain are indicated on the left-hand side of the blot. C, the solubilized cell lysate from each group of transfected HEK 293 cells (≈60 µg protein loaded per well) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analysed by Western blot, using the anti-BKCa channel antibody. The band corresponding to the expressed BKCa channel α subunit detected in the solubilized HEK 293 cell lysates is indicated on the left-hand side. In A-C, the electrophoretic mobilities of molecular mass standards (size in kDa) are shown on along the right-hand side of each blot. The results shown in this figure are representative of data observed in two additional experiments.
