Figure 2. Postsynaptic depolarisation due to hypoxia is modulated by GABAB receptor inhibition.
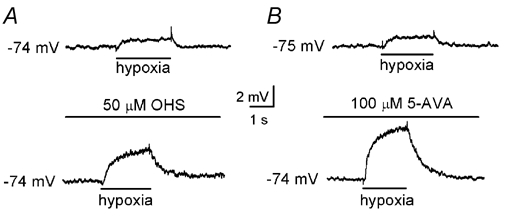
A, typical current-clamp recordings made from a petrosal neurone juxtaposed to a type I cluster in co-culture. Application of hypoxia (PO2, 5 mmHg) is indicated by the horizontal bar below each trace. Under control conditions (upper), hypoxia induced a postsynaptic depolarisation which was increased in the presence of the GABAB receptor antagonist, OHS (50 µm; lower). B, as in A, except the effect of a further specific GABAB receptor antagonist, 5-aminovaleric acid (5-AVA; 100 µm), was examined.
