Figure 4. Effects of the Ca2+ channel inhibition on distension-induced vasodilatation.
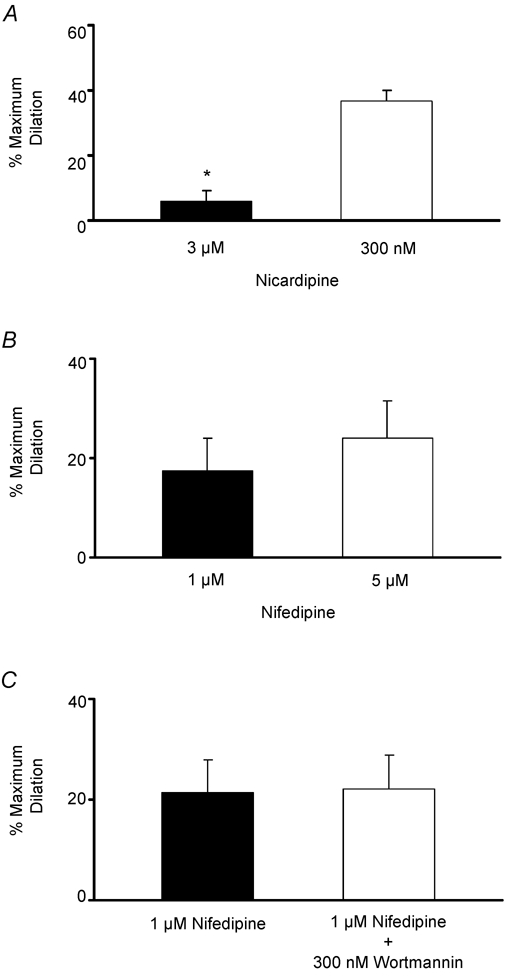
A, summary of the mean dilatations evoked by balloon distension (3 distensions, 1 Hz, duration ≈0.5 s) in the presence of nicardipine (3 μm) compared to those obtained in a separate group of preparations receiving nicardipine (300 nm), demonstrating that responses were inhibited by the higher concentration (n = 9 for each concentration, *P < 0.01). B, summary of mean dilatations evoked by balloon distension (3 distensions, 1 Hz, duration ≈0.5 s) in the presence of 1 μm nifedipine. Following a 10 min washout, responses were re-examined in the same preparations in the presence of 5 μm nifedipine and similar responses were obtained (n = 5). C, summary of mean dilatations evoked by balloon distension (3 distensions, 1 Hz, duration ≈0.5 s) in the presence of 1 μm nifedipine. Following a 10 min washout, responses were re-examined in the same preparations in the presence of nifedipine (1 μm) and wortmannin (300 nm) and similar responses were also obtained (n = 5). Arterioles were preconstricted with PGF2α, as described in Fig. 1.
