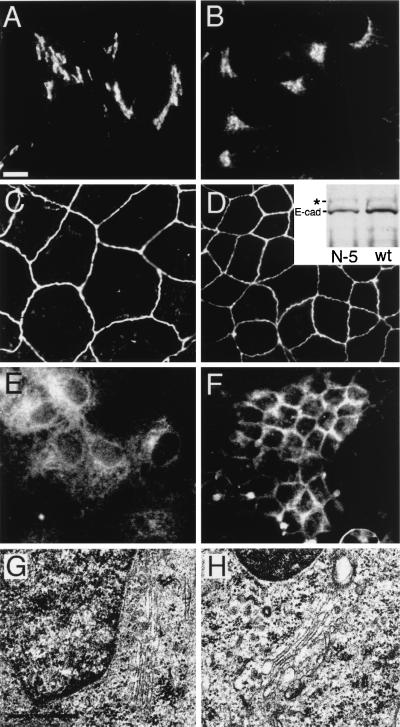
Figure 4.
Comparison of the effect of βIN−5 spectrin on Golgi and the assembly of different proteins in MDCK cells. Wild-type (B, D, F, H) and βIN−5-transfected cells (A, C, E, and G) are shown. The localization of VSV-G protein (E and F) was measured after transient infection. E-cadherin (C and D) was monitored with a Mab from Transduction Laboratories and also by the extent to which the precursor peptide was proteolyzed (Inset, Western blot) from 135 kDa (∗) to 120 kDa (E-cad) (a process that occurs in the trans-Golgi 26). There was no significant difference in the extent of E-cadherin processing or its level of assembly at the plasma membrane in the βIN−5 line vs. wt cells. Despite the disruption of Na,K-ATPase and VSV-G transport (and the wt Golgi spectrin skeleton; Fig. 3), the Golgi appears to remain largely intact as measured by the distribution of β-COP (A and B) and by the presence of normal-appearing juxtanuclear Golgi structures in uranyl acetate and lead-stained electron microscopy (G and H). [Bar = 10 μ (A–F) and 0.5 μ (G and H)]. [Original magnification = ×63,000 (G and H)].