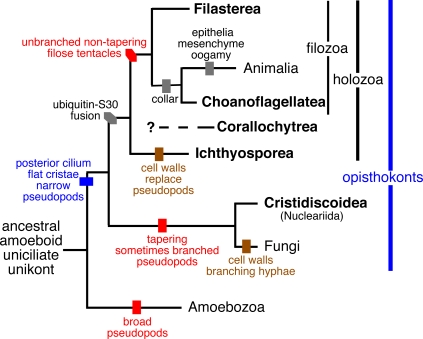
Figure 3. Evolutionary relationships among animals and fungi and their closest unicellular relatives (Choanozoa, Protozoa).
The five choanozoan classes (bold) form at least four distinct clades, one probably related to fungi and the others to animals. Innovations in pseudopod character and their multiple losses with the origin of cell walls during nutritional shifts from engulfing prey (phagotrophy) to saprotrophy or parasitism are indicated by bars. In the common ancestor of animals and choanoflagellates a subset of the filozoan actin-supportd tentacles aggregated as a collar around the cilium ( = flagellum) for filter feeding. Epithelia and connective tissue made the first animals: the filter-feeding sponges.