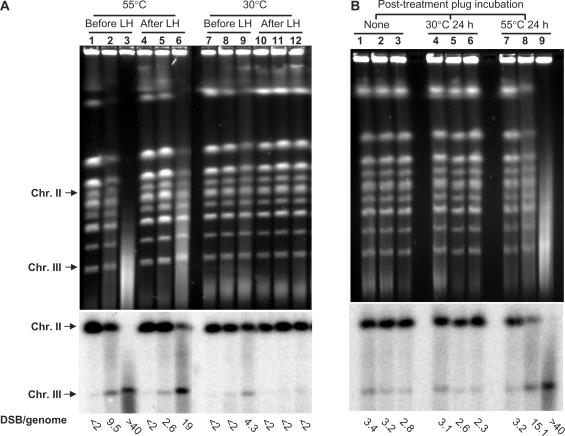
Figure 3.
PFGE of yeast chromosomes after MMS treatment. The calculated number of chromosome breaks is shown under each lane. (A) MMS-treatment of yeast cells induces heat-labile base damages that can be detected by formation of secondary DSBs. G1 haploid yeast were treated with 0.1% MMS for 15 min (lanes 2, 5, 8, 11) or 30 min (lanes 3, 6, 9, 12) followed by immediate DNA purification and PFGE (lanes 1–3 and 7–9) or PFGE after LH or 24 h in a buffer (LH) (lanes 4–6 and 10–12); lanes 1, 4, 7 and 10 are mock-treated controls. DNA purification with proteinase K digestion was performed either at 55°C (lanes 1–6) to measure heat-dependent breaks (HDBs) or at 30°C (lanes 7–12) to measure heat-independent breaks (HIBs). Chromosomes were visualized by ethidium bromide staining and breaks were quantified based on Southern hybridization. The numbers of DSBs per haploid yeast genome, calculated as described in the text are shown under each lane. (B) MMS treatment of chromosomal DNA within the plug produces heat labile sites. Plugs containing genomic DNA from G1 were treated with 11.8 mM MMS for 15 min (lanes 2, 5, 8) or 30 min (lanes 3, 6, 9); lanes 1, 4 and 7 are mock-treated controls. Lanes 1–3 contain DNA-plugs with no post-treatment incubation; lanes 4–6 contain DNA-plugs that were post-incubated at 30°C for 24 h; lanes 7–9 contain DNA-plugs that were post-incubated at 55°C for 24 h.