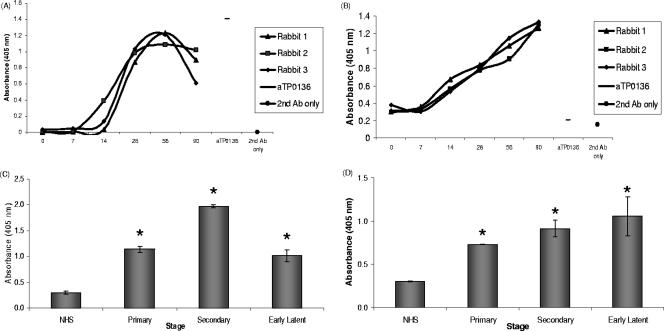
FIG. 5.
Reactivity of serum antibodies (Ab) from experimentally infected rabbits and human syphilis patients with purified rTP0136 protein, as determined by ELISA. (A) Reactivity of sera from individual rabbits (each indicated by a separate line) collected at sequential time points during an experimental T. pallidum infection with rTP0136 protein. Prechallenge rabbit sera (zero time) were used as a negative control, and anti-rTP0136 (aTP0136) antibody was used as a positive control for ELISA well coating. (B) Reactivity of individual rabbit sera to a protein lysate of T. pallidum was used as a control for the sensitivity of the rabbit sera used for panel A. As in panel A, prechallenge rabbit sera (zero time) were used as a negative control and anti-rTP0136 (aTP0136) was used as a positive control for plate coating. (C) Purified rTP0136 reactivity with immunoglobulin from sera pooled from patients with primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis. NHS were used as a negative control. (D) Reactivity of pooled human sera to the T. pallidum protein lysate was used as a positive control for the reactivity of the sera used for panel C. As in panel C, NHS were used as a negative control. Human serum samples were diluted 1:200, and rabbit samples were diluted 1:100. Statistical significance (P < 0.005) in comparison with negative controls (NHS) or prechallenge sera by the Student two-tailed t test is indicated by an asterisk.