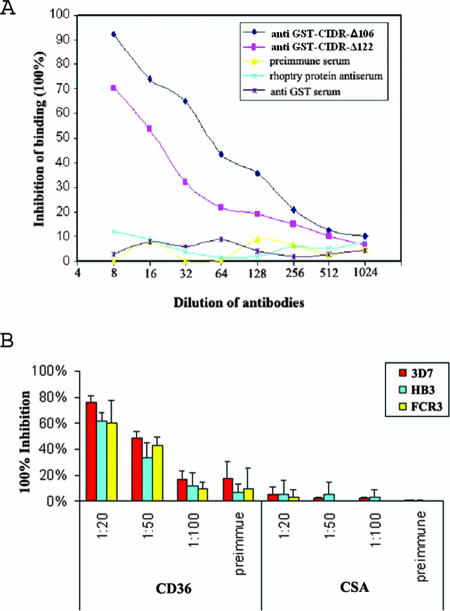
FIG. 6.
(A) Antiserum inhibition assay. Sera raised against GST fused with CIDR-Δ106 and GST fused with CIDR-Δ122 were tested for inhibition effects on CIDR-f and CD36/Fc binding. The percentage of binding inhibition was calculated as the ratio of the OD405 of a control sample (without any serum) to the OD405 of each sample with various serum dilutions. (B) Blockade of CD36-adherent PEs of strains 3D7, HB3, and FCR3 using murine polyclonal antisera against CIDR-Δ106. PEs were preincubated with binding buffer alone or binding buffer containing antisera diluted from 1:20 to 1:100 or preimmune sera. After 30 of min incubation, the PEs were added to HLECs or CHO-K1 cells and tested for binding. The average number of PEs bound to 100 HLECs or CHO-K1 cells in three microscopic fields (magnification, ×40) was calculated. The percent inhibition of parasite binding compared to that for the untreated control without any added proteins was determined. Standard deviations were determined from three independent experiments.