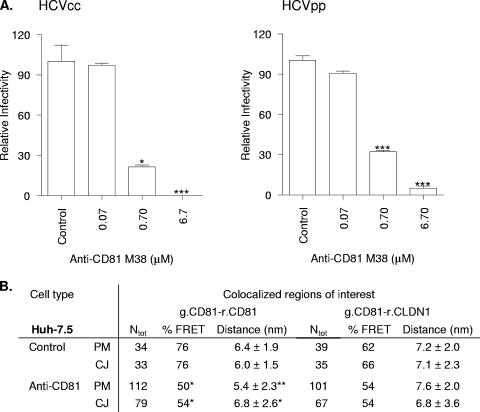
FIG. 7.
Effect of anti-CD81 on FRET between fluorescently N terminus-tagged CD81 and CLDN1 and viral infectivity. (A) Huh-7.5 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of anti-CD81 MAb (M38) for 1 h at 37°C. Control and M38-treated cells were infected with HCVcc strain JFH-1 or HCVpp for 1 h, unbound virus was removed by washing, and cells were incubated at 37°C for 72 h. M38 significantly reduced HCVcc and HCVpp infectivity (*, P < 0.05 [Dunn's test]). Data are expressed as relative infectivities compared to control untreated cells and represent the means from three replicate infections. (B) Huh-7.5 cells expressing g.CD81/r.CD81 or g.CD81/r.CLDN1 were incubated with anti-CD81 M38 (2 μM) or isotype-matched control MAb for 1 h at 37°C at a concentration shown to saturate cell-surface-expressed CD81 by flow cytometry. Cells were fixed, and regions of colocalization at the nonjunctional PM and CJs were imaged by confocal microscopy. The numbers of colocalized regions analyzed (Ntot), the %FRET values, and the estimated distances between fluorescent proteins are shown. M38 significantly reduced the %FRET and estimated distances between CD81-CD81 (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 [Fisher's exact test and Mann Whitney test]).