Fig. 5.
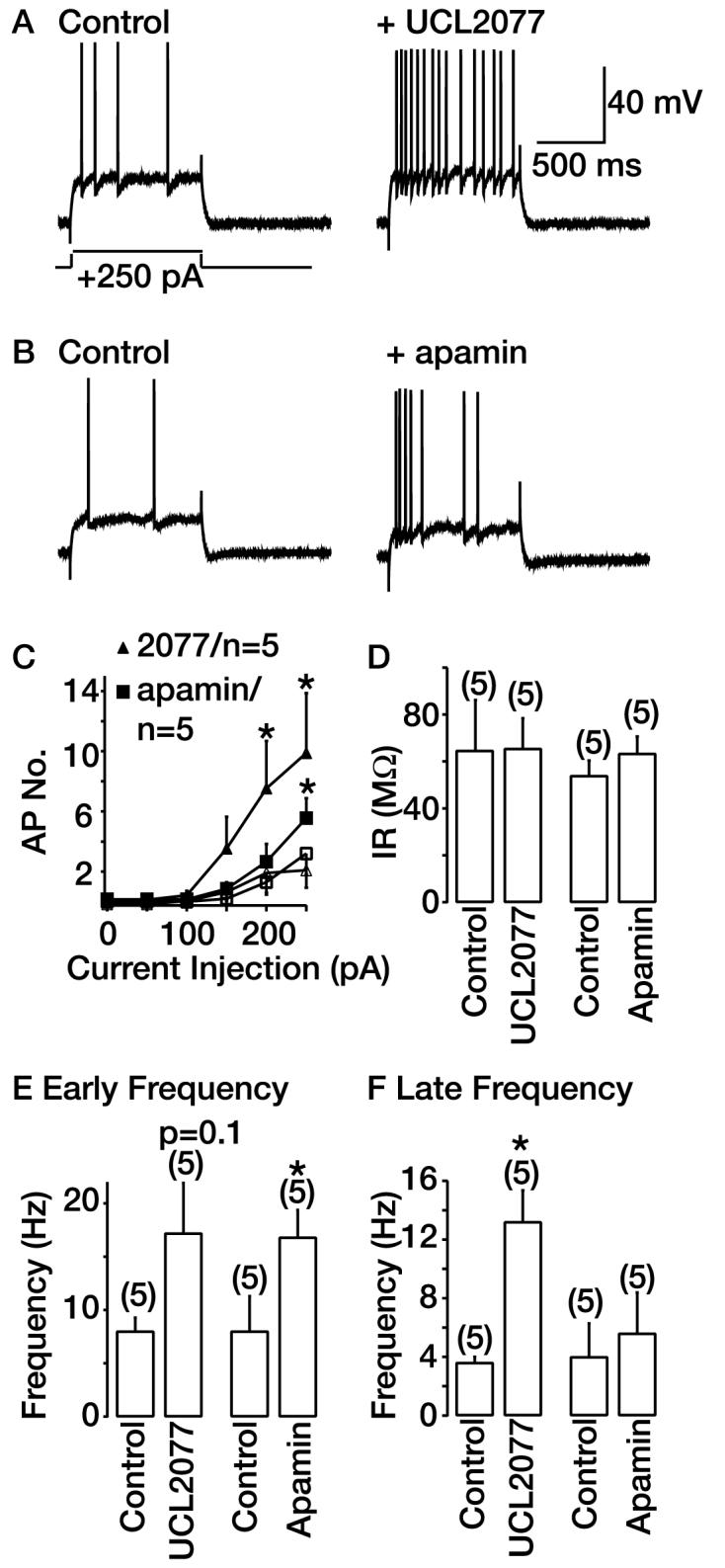
Comparison of effects of UCL2077 and apamin on spike frequency adaptation in hippocampal neurons. A and B, typical effects of 10 μM UCL2077 and 100 nM apamin on spike-firing when a 250-pA depolarizing pulse is applied from −70 mV. The scale bars shown in A apply to B. C, graph depicting action potential (AP) number produced by current pulses in the absence (open symbols) and presence (closed symbols) of 10 μM UCL2077 or 100 nM apamin. D, E, and F, graphs show the effects of 10 μM UCL2077 and 100 nM apamin on input resistance (IR) and spike frequency within the first 250 ms (E) or the last 250 ms (F) of a 1-s step. *, significance at p < 0.05.
