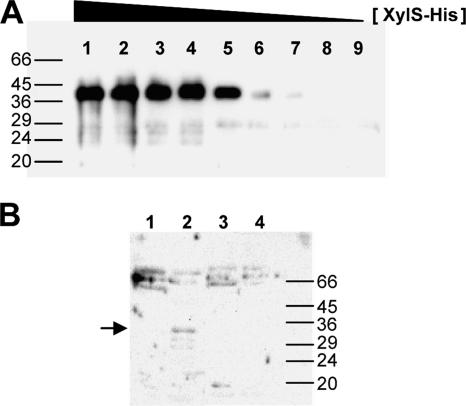
FIG. 2.
Heparin chromatography of XylS-containing extracts and estimation of XylS concentration in the extracts. (A) XylS was purified from inclusion bodies after solubilization with 6 M guanidium, renaturing, and His-affinity chromatography. It is worth noting that XylS protein obtained with this protocol was inactive. Samples of known XylS concentration (5, 3.5, 2.5, 1.5, 1, 0.5, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 μg loaded in lanes 1 to 9, respectively) were separated by denaturing sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with antibodies at a dilution of 1/1,000 against XylS (76). (B) Cell extracts (170 μg of total protein) of E. coli CC118 (pLOW2::XylS) (lanes 1 and 2) or E. coli CC118 (pLOW2) (lanes 3 and 4) were loaded in a 1-ml heparin column, and samples were eluted as indicated in Materials and Methods. Lanes 1 and 3, whole extract; lanes 2 and 4, extract eluted from the column. Molecular weight markers were BSA (66 kDa), ovalbumin (45 kDa), pepsin (36 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa), trypsinogen (24 kDa), and trypsin inhibitor (20 kDa).