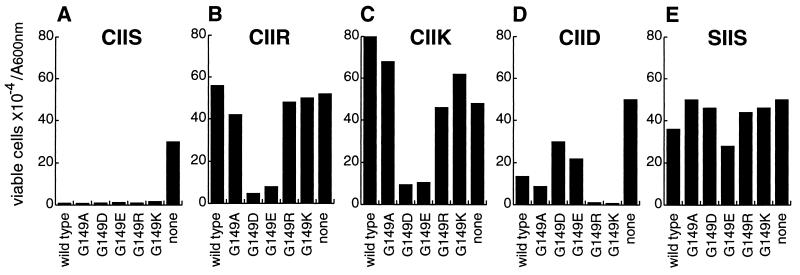
Figure 4.
Ram1p variants of farnesyltransferase exhibited allele-specific differences in the ability to prenylate Ras2val19 substrate variants in vivo. A ram1Δ strain (JRY5393) was transformed with plasmid YCpL-RAM1-ApaI (wild type), vector YCplac111 (none), or with a mutated YCpL-RAM1 plasmid that encoded a Ram1p variant with the indicated substitutions for glycine-149. The seven resulting strains were then transformed with plasmids, derived from pJR1056, that encode variants of Ras2val19 protein that differed in their CaaX sequences, as indicated. Wild-type Ras2val19 terminates with cysteine–isoleucine–isoleucine–serine (Ras2val19–CIIS; A). Variants that differed from wild type had the C-terminal serine substituted with arginine (Ras2val19–CIIR; B), lysine (Ras2val19–CIIK; C), or aspartate (Ras2val19–CIID; D). The Ras2val19–SIIS variant (E) could not be prenylated due to substitution of serine for cysteine-319, which is the prenyl lipid acceptor. To assess the extent of prenylation, viability of each strain following nutrient deprivation was determined following growth for 5 days at 25°C in liquid minimal medium lacking leucine and uracil (to select for the LEU2 and URA3 plasmids). Data are presented as viable cells × 10−4 per A600nm unit.