Figure 3.
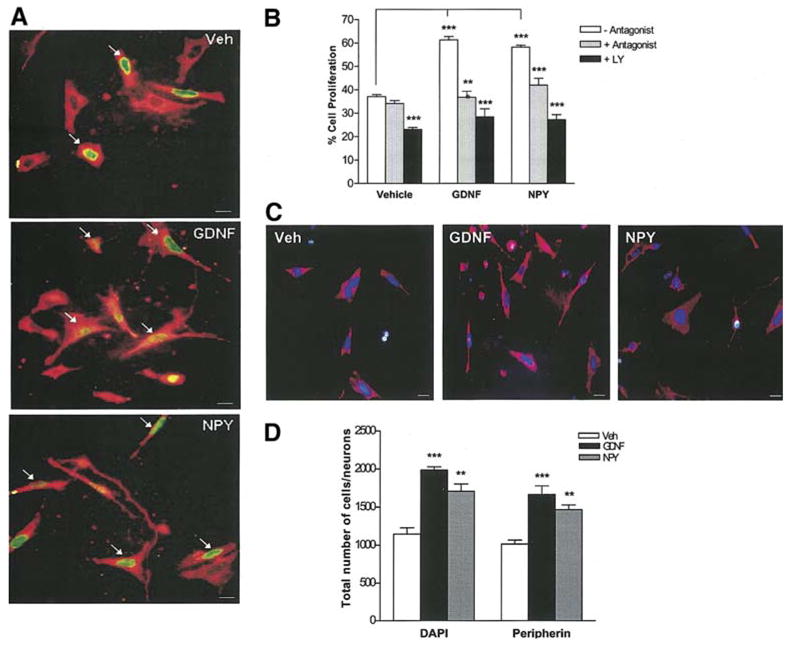
GDNF induces proliferation of enteric neurons through NPY. (a, b) Enteric neurons treated with vehicle, NPY or GDNF in the presence or absence of either the NPY-Y1 receptor antagonist (BIBP3226) or the PI-3-kinase inhibitor (LY294002) were maintained in culture for 48 h and fixed. BrdU was added to the medium 24 h prior to fixation. The % of BrdU+ (green)/peripherin+ (red) neurons was determined to assess proliferation. Arrows point to the BrdU+ neurons. Exposure of enteric neurons to NPY (48 h) significantly increased proliferation similar to GDNF. GDNF- and NPY- induced proliferation of enteric neurons was inhibited by both BIBP3226 and LY294002, n=4. Scale bar: 20 μm. (c, d) The total number of cells (DAPI-blue) and neurons (peripherin-red) per well was assessed under the stated culture conditions, n=2. Results are mean + S.E., *** = p<0.001, ** = p<0.01. P value is with respect to the neurons cultured in the absence of antagonist (b) or vehicle (d) in each respective condition.
