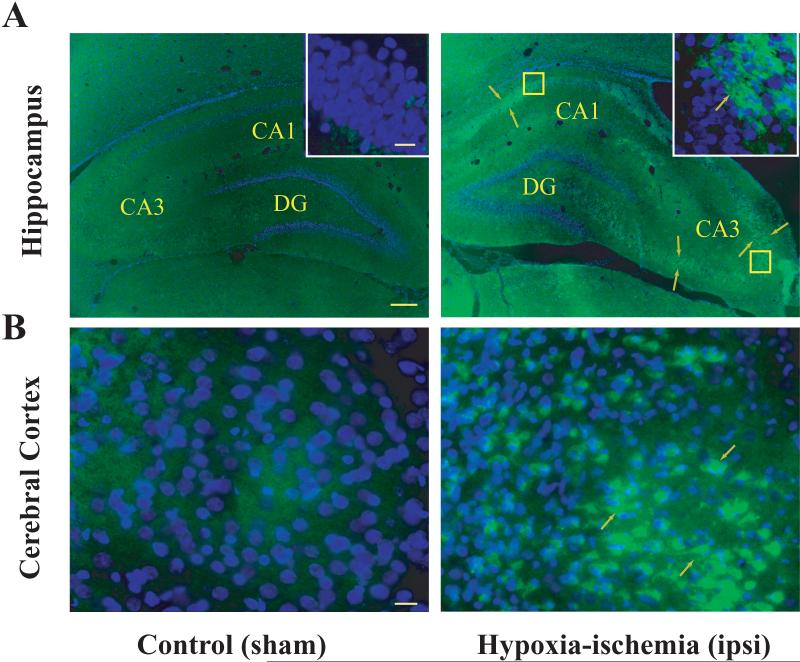
Figure 2.
Induction of NP1 in the ipsilateral hippocampus and cerebral cortex of neonatal rat brain following HI. Neonatal rats were sacrificed at indicated time after HI exposure. Representative coronal brain sections (20 μm) from sham controls and HI brains were immuno-stained using mouse anti-rat NP1 monoclonal primary antibody (1:500) (BD Transduction laboratories, CA) and FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (1:500) (Jackson ImmunoResearch) as described previously (Hossain et al. 2004). A high level of NP1 immunoreactivity was observed in the pyramidal layer of CA3 and CA1 but not in the dentate gyrus of the ipsilateral hippocampus and in the frontal and parietal cortex relative to sham controls. Immunofluorescence analyses were performed using a fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss Axioplan 1 microscope fitted with AxioVision 3.0 software). NP1 specific immunofluorescence (green) from representative brain sections is shown (arrows) at low (5 ×) and high (100 ×) magnifications. Scale bar: A, 200 μm; B and inset 20 μm.