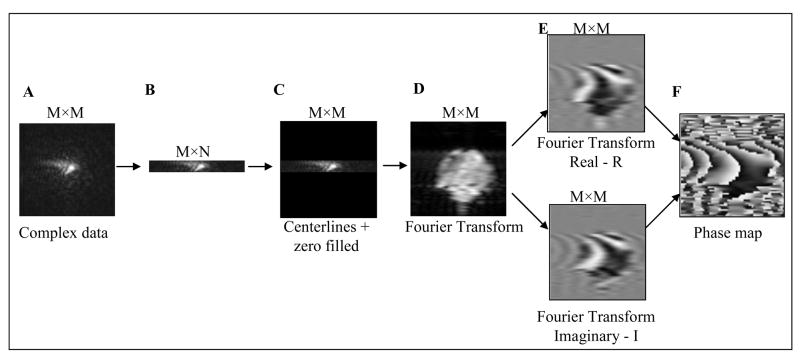
Figure 1.
Phase map calculation using an arbitrary number of k-space lines. A) Complex data in k-space after time-reversal and ghost correction; B) Extraction of N centerlines in k-space; C) Zero–filling of M x N matrix; D) Amplitude image after Fourier- transformation; E) Real and imaginary parts of a complex image; and, F) Phase image (Arc-tangent of the imaginary part-to-real part ratio). The K-space maps show the magnitude only.