Figure 3.
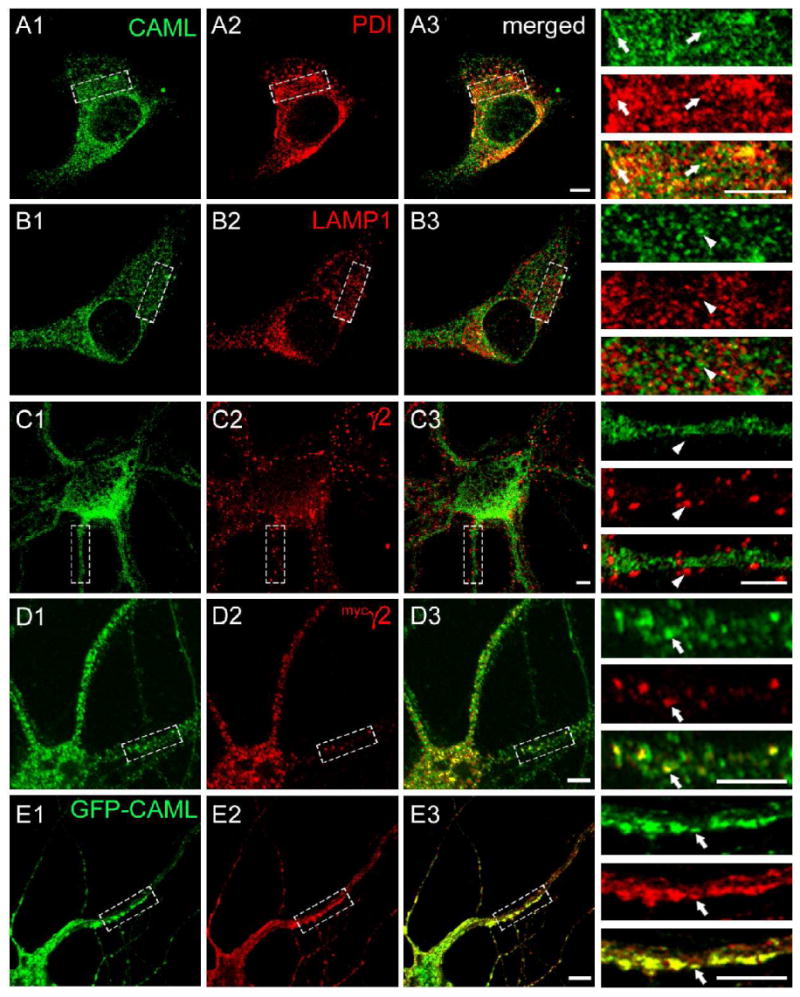
Colocalization of CAML and the γ2 subunit in an intracellular compartment. A-C. Cultured cortical neurons (DIV 18) were fixed, permeabilized and subjected to immunofluorescent staining for CAML (A1, B1, C1, green) together with the ER marker PDI (A2, red), the lysosomal marker LAMP1 (B2, red), or the endogenous γ2 subunit (C2, red) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Merged images are shown in A3, B3 and C3, respectively, with enlarged bracketed areas of each panel depicted on the right. Note the extensive colocalization of punctate CAML immunoreactivity with staining for the ER marker PDI (A3), whereas there is no discernable colocalization of CAML with lysosomal LAMP1 (B3) or punctate immunoreactivity for the γ2 subunit (C3), representative of postsynaptic GABAARs. D, E. Cortical neurons (DIV16) were transfected with the mycγ2 subunit (D) or GFP-CAML and mycγ2 (E). At DIV18 they were fixed, permeabilized and imaged as above and analyzed for colocalization of immunoreactivity for endogenous CAML (D1, green) or GFP-CAML fluorescence (E1, green) with immunoreactivity for mycγ2 (D2, E2, red). Note the extensive colocalization of punctate intracellular mycγ2 immunoreactivity with vesicular immunoreactivity or GFP fluorescence representing CAML, in both the soma and dendrites of merged images (D3, E3) and detailed in the enlarged dendritic segments. Arrowheads point to lack of colocalization, arrows point to colocalized γ2 subunit and CAML signals. Scale bars, 5 μm.
