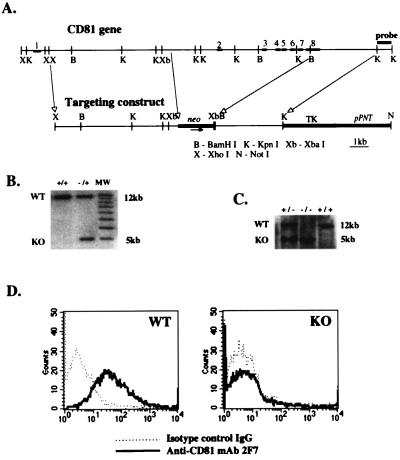
Figure 1.
Generation of CD-81-deficient mice. (A) Structure of the CD81 gene (Upper) and of the targeting construct (Lower). Exons are represented by bold segments and are numbered. neo, neomycin resistance gene. (B) Southern blot analysis of DNA from ES cell clones. Genomic DNA was digested by XbaI and probed with the KpnI fragment shown in A. The wild-type (WT) allele is represented by the 5-kb band. (C) Southern blot analysis of DNA from tails of littermate mice of brother-sister mating of CD81 heterozygotes (+/−) mice. Analysis was performed as in B. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of surface expression of CD81 on thymocytes from WT and CD81-deficient (KO) mice. Cells were stained with biotinylated anti-CD81 hamster mAb 2F7 (——) or biotinylated hamster IgG as an isotype control (· · · ·) followed by streptavidin-PE.