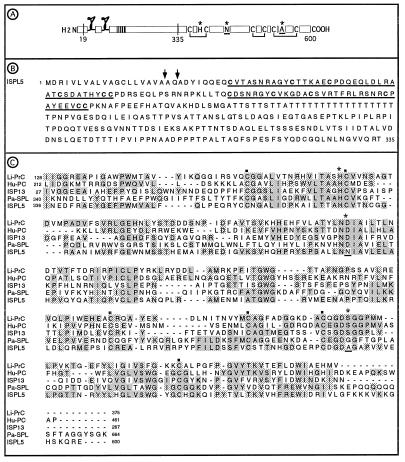
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic sequence features of full-length ISPL5 showing the proposed signal peptide cleavage site (amino acid 19), the putative cysteine knots, the polythreonine stem region (vertical stripes), the putative activation site (amino acid 335), cysteines and disulfide bridges that are conserved in serine proteases, and the catalytic triad (∗) with two nonconserved residues underlined. (B) The amino terminal region of ISPL5 with the putative cysteine knots underlined. Two possible signal peptide cleavage sites are marked with arrows. (C) ISPL5 serine protease domain compared with ISP13 (accession no. Z69978), Limulus (Tachypleus tridentatus) clotting factor 2, which converts coagulen to insoluble coagulen gel (Li-PrC, accession no. P21902), human blood coagulation regulator protein C (Hu-PC, accession no. P04070), and Pacifastacus leniusculus (crayfish) hemocyte-specific serine protease-like protein (Pa-SPL, unpublished data; accession no. Y11145). The six conserved cysteines of serine proteases are marked with ▪; the residues of the serine protease catalytic triad are marked with ∗, with the nonconserved residues underlined as in A above. Aligned residues that match in two or more sequences are shaded. Numbers indicate position of residues from the N terminus.