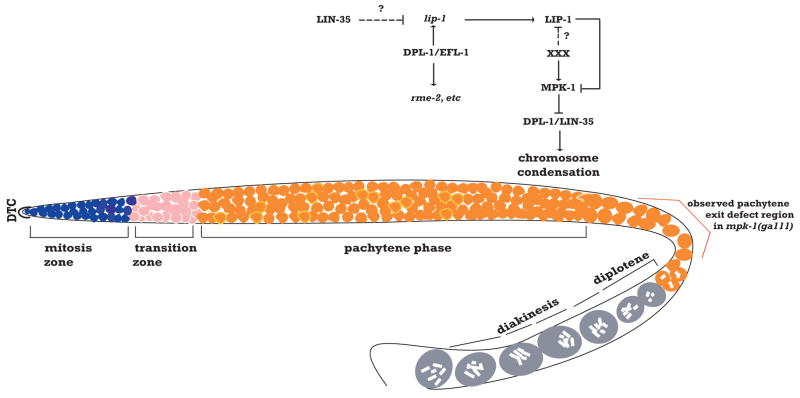
Figure 7. Model for mutual regulatory relationship between the Rb/E2F and MAP kinase pathways in the C.elegans germ line.
In this model, depending on the place and time in germ cell development, MAP kinase either controls DPL-1 function or vice versa. DPL-1 can exist in a regulatory complex with EFL-1 to promote lip-1 expression in mid-pachytene. XXX represents an unknown external signal that results in spatially-restricted activation of MAP kinase, possibly through blocking LIP-1 function. Once cells move beyond reach of the signal, LIP-1 inactivates MPK-1 in the proximal gonad. DPL-1 might also exist in a separate complex with LIN-35 to promote chromosome condensation. This complex is inhibited by MAP kinase in late pachytene through phosphorylation of DPL-1 to promote normal chromosome morphology.