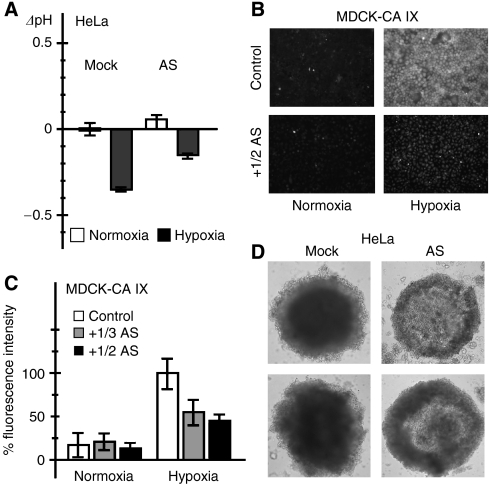
Figure 4.
Effect of overexpressed AS variant on acidification, inhibitor binding, and spheroid formation. (A) The AS-transfected HeLa cells and related mock-transfected controls were incubated for 48 h in normoxia and hypoxia, respectively, and extracellular pH was measured in culture medium immediately at the end of experiment. Data are expressed as differences between the pH values (ΔpH) measured in normoxic vs hypoxic cells and include standard deviations. Results show that expression of AS reduces the acidification mediated by FL CA IX protein under hypoxia. (B) MDCK-CA IX transfected cells that constitutively express human FL CA IX protein were treated for 48 h by a fluorescent CA inhibitor (FITC-CAI) in the absence (control) or in the presence of the secreted AS variant added with the conditioned medium from MDCK-AS transfectants. Conditioned medium was mixed with a fresh cultivation medium. FITC-CAI bound only to hypoxic cells and was considerably reduced in the presence of the AS protein. (C) The same experiment was performed repeatedly with either one-half (1/2 AS) or one-third (1/3 AS) of conditioned medium from MDCK-AS cells. Binding of FITC-CAI and corresponding fluorescence was evaluated from acquired images using Scion Image software. Data were expressed as a percentage of positive control represented by hypoxic MDCK-CA IX cells incubated with FITC-CAI in the absence of AS. The results confirmed that AS reduces the binding of FITC-CAI to CA IX. (D) Microscopic images of spheroids grown from control mock-transfected HeLa cells and from AS-transfected HeLa cells, respectively. Control HeLa cells express hypoxia-induced, functional FL CA IX protein, and produce spheroids that form compact cores. HeLa-AS cells, which contain both hypoxia-induced FL CA IX and constitutively expressed AS, contain loose cores possibly due to AS-compromised function of FL leading to decreased survival of hypoxic core cells.