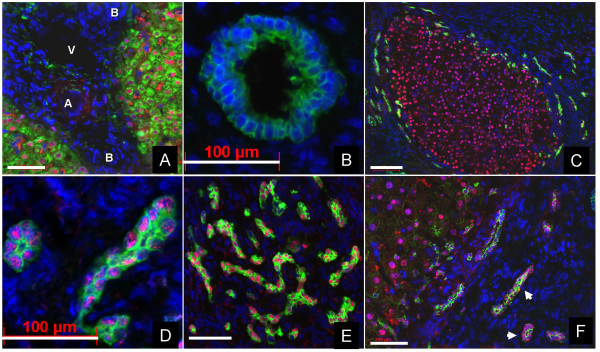
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemical analysis of Prox1 in normal human liver, in cirrhotic livers and in hepatocellular carcinoma. A) Double immunofluorescent labeling of HepPar1 (green), Prox1 (red) and cell nuclear counterstaining with DAPI (blue) in normal human liver shown combined. A: Arteria, B: Bile duct, V: Vena. Bars represent 100 μm. B) Increased magnification of a bile duct within a normal human liver. Double immunostaining was performed with anti-CK7 (green) and anti-Prox1 (red). The blue staining with DAPI represents the nuclei. Bars represent 100 μm. C) Immunohistochemical staining of a regenerative nodule in a cirrhotic liver with anti-CK7 (green), anti-Prox1 (red) antibodies and cell nuclear counterstaining with DAPI (blue), shown combined. Bars represent 100 μm. D) Double immunostaining of CK7 (green) and Prox1 (red) in ductular cells within a fibrotic septum of a cirrhotic liver, cell nuclear counterstaining with DAPI (blue) shown combined. Bars represent 100 μm. E) Double immunostaining of CK19 (green) and Prox1 (red), cell nuclear counterstaining with DAPI in cells with a ductular phenotype within a cirrhotic liver shown combined. Bars represent 100 μm. F) Immunohistochemical reactions of OV-6 (green) and anti-Prox1 (red) antibodies in HCC and the fibrous septa. The blue staining with DAPI represents the nuclei. Prox1+ hepatocytes within the neoplastic nodule are surrounded by OV-6+ ductular cells. Note that OV-6+ cells are simultaneously Prox1+ (white arrows). Bars represent 100 μm.