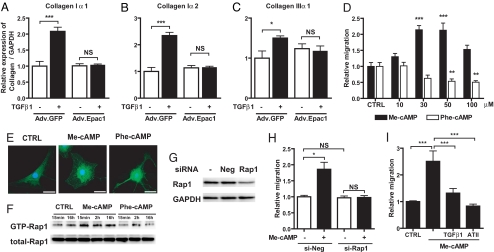
Fig. 2.
Effect of Epac on collagen synthesis, migration and morphology in cardiac fibroblasts. (A–C) Fibroblasts were infected with Adv.GFP or Adv.Epac1 in serum-free media for 24 h and then with or without TGFβ1 (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cells were assayed by using real-time RT-PCR to quantify collagen Iα1, Iα2, and IIIα1; the data are normalized to GAPDH. n = 4. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. (D) Fibroblast migration was examined by using a modified Boyden chamber method in the absence (CTRL) or presence of Me-cAMP, an Epac-activator, or Phe-cAMP, a PKA-activator. Data are shown as the fold-increase relative to control. n = 6–8. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 compared with control (CTRL). (E) Immunocytochemistry was performed by using cardiac fibroblasts (passage 1) grown for 48 h in serum-free media and then for 1 h in serum-free media alone (CTRL) or together with Me-cAMP or Phe-cAMP. Cells were stained for Epac1 (green) and nuclear staining of DNA with DAPI (blue). (Scale bar, 30 μm.) (F) Time-dependent Rap1 activation in cardiac fibroblasts. Cells were serum-starved for 48 h, then incubated with Me-cAMP (50 μM) or Phe-cAMP (50 μM) up to 16 h and assayed for Rap1 activation. Precipitates (Upper) and total cell lysates (Lower) were analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Rap1 antibody. (G) siRNA-promoted silencing of Rap1 protein expression. Fibroblasts were incubated with Rap1-targeted siRNA for 24 h, lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with a Rap1 antibody. (H) Fibroblasts were incubated with Rap1-targeted siRNA for 24 h, treated with Me-cAMP (50 μM) and migration was assayed. n = 4–6; *, P < 0.05. (I) Migration was examined in cardiac fibroblasts treated with Me-cAMP (50 μM) alone, or together with TGFβ1 (10 ng/ml) or angiotensin II (100 nM). n = 4–7, ***, P < 0.001.