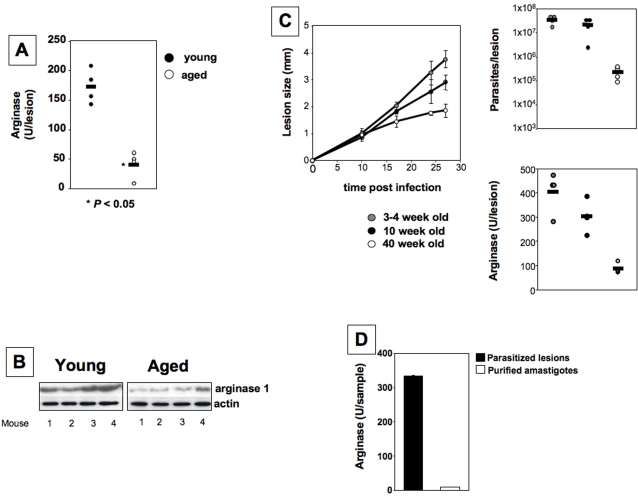
Figure 4. Higher arginase activity at the site of pathology correlates with exacerbation of disease.
Groups of young (6–8 weeks) and older (12 months) BALB/c mice were infected with 2×106 L. major promastigotes in one hind footpad. Four weeks post infection, the infected footpads were harvested and the level of arginase activity was determined by enzymatic assay (a) or western blot (b). (c) Groups of pre-pubertal mice (3–4 weeks), adult (10 weeks) or older (40 weeks) BALB/c mice were infected with 2×106 L. major promastigotes in one hind footpad and the lesion development was monitored by measuring the increase in footpad thickness at regular intervals; the error bars represent standard error of the mean (left panel); 4 weeks post infection, the infected footpads were harvested and the parasite load (upper right panel) and arginase activity (lower right panel) were measured. (d) BALB/c mice were infected with 2×106 L. major promastigotes in one hind footpad. Four weeks post infection, the infected footpads were harvested and arginase activity was determined both in the footpads and in the amastigotes purified from the footpads. The horizontal bar represents the average value and data show the results of one representative experiment out of three independent experiments.