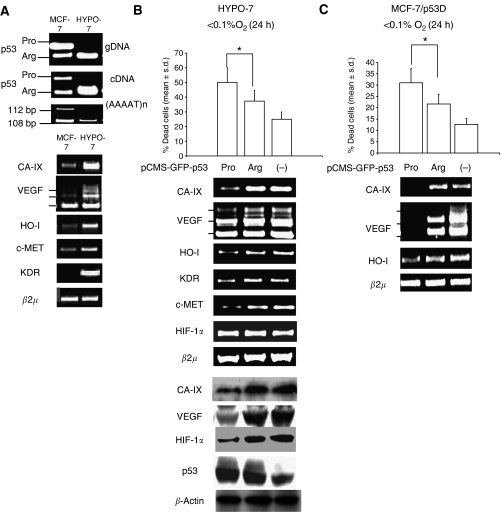
Figure 3.
The p53Arg is retained in MCF-7-derived hypoxia-selected clones. (A) HYPO-7 and MCF-7 cells: PCR analysis of p53 codon 72 genotype on genomic DNA (gDNA) and cDNA, Loss of heterozygosity at the (AAAAT)n pentanucleotide repeat located in the Intron I of the TP53 gene (upper); RT-PCR analysis of CA-IX, VEGF, HO-I, c-MET, KDR and β2 μm RNA level (lower). (B) HYPO-7 cells exposed to <0.1% O2 for 24 h and transiently transfected with p53Arg, p53Pro (-) pCMS-GFP vector: Cell death analysis (n=3), *P=0.028; Bonferroni-corrected post hoc test, data are expressed as mean±s.d. (upper); RT-PCR analysis of CA-IX, VEGF, HO-I, KDR, c-MET, HIF-1α and β2 μm RNA level (middle); Western blot analysis of CA-IX, VEGF, HIF-1α, p53 and β-actin (lower). (C) pBabe-p53D stably transduced MCF-7 (MCF-7/p53D), exposed to <0.1% O2 for 24 h, and transiently transfected with p53Arg, p53Pro or (-) pCMS-GFP vector: cell death analysis (n=3), *P=0.035; Bonferroni-corrected post hoc test, data are expressed as mean±s.d. (upper); RT-PCR analysis of CA-IX, VEGF, HO-I and β2 μm RNA level (lower). Transfection efficiency was evaluated by fluorescent microscopy analysis of GFP positive cells (data not shown).