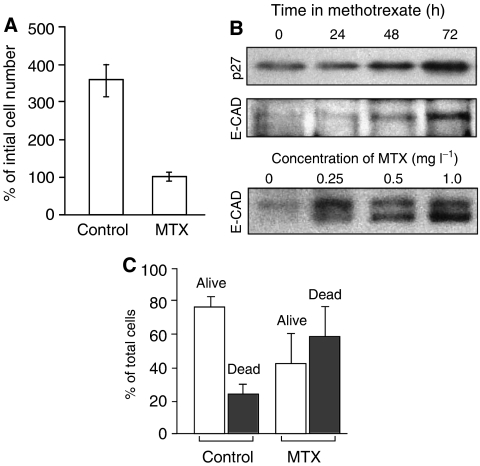
Figure 2.
Effect of MTX upon LNCaP growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. (A) Inhibition of cell growth by MTX. LNCaP cells were incubated for 72 h in medium containing 1 mg l−1 MTX, or solvent alone (control). Proliferation is indicated by a 350% net increase in cell number at 72 h vs no increase with MTX. Mean of two experiments carried out in duplicate, ±s.d. (B) Western blots of LNCaP cells incubated in the presence of MTX, and analysed with specific antisera to growth arrest marker (p27/kip-1; upper panel) and a differentiation marker (E-cadherin; lower panels). The upper panels show a time course of induction at a fixed MTX concentration (1 mg l−1); the lower panel shows a dose–response study with a fixed incubation time of 72 h. The E-cadherin doublet at 124 and 135 kDa (lower panel; Bis–Tris gel) was not well resolved on the smaller, Tris-glycine gel (middle panel). (C) Analysis of apoptosis in LNCaP cells after incubation with MTX. Cells were incubated for 72 h in the presence or absence of MTX, as indicated. Adherent and nonadherent cells were pooled and analysed by FACS analysis. The sub-G1 fraction (apoptotic cells, closed bars) and the G1+S+G2/M fractions (living cells, open bars) were expressed as a percentage of total cell number. Bars show mean of six experiments±s.d.