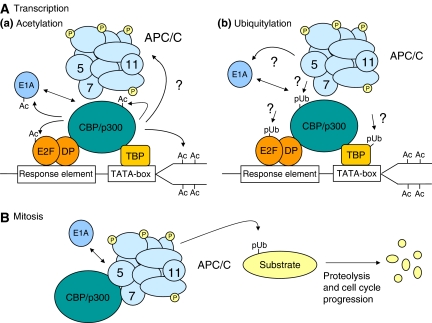
Figure 2.
Role of APC/C–CBP/p300 complexes in transcription and cell-cycle control. (A(a)) Transcription and acetylation. Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein/p300 function as transcriptional coactivators for sequence-specific DNA-binding transcription factors. These enzymes acetylate histones to alter chromatin accessibility. Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein/p300 also acetylate transcription factors to regulate their activity. Interaction with E1A or the APC/C potentially interferes and/or retargets this activity and E1A is itself a substrate for acetylation. Anaphase-promoting complex5 and/or APC7, as components of the APC/C holoenzyme, interact with CBP/p300 to stimulate inherent CBP/p300 acetyltransferase activity, and CBP/p300-dependent transcriptional activity. Early region 1A might disrupt or mimic APC/C function in this regard through its interaction with CBP/p300. (A(b)) Transcription and ubiquitylation. The recruitment of the APC/C to target promoters could potentially regulate CBP/p300 function by promoting CBP/p300 ubiquitylation. The ubiquitylation of the CBP/p300 in this instance could directly affect CBP/p300 acetyltransferase activity, and/or affect CBP/p300 interaction with other proteins, and/or promote proteasomal-mediated degradation of CBP/p300. Early region 1A could interfere with APC/C function in this regard by binding directly to CBP/p300. (B) Mitosis. The APC/C complex ubiquitylates cell-cycle regulatory proteins and targets them for proteasomal degradation. Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein functions as an E4 ligase in this regard. Whether acetylation of the APC/C by CBP/p300 regulates APC/C E3 ligase activity in this regard requires further investigation. We propose that E1A might regulate mitotic progression and/or promote genomic instability through interfering directly with APC/C function in mitosis through its ability to bind CBP/p300. Ac, acetylated-residues; pUb, polyubiquitylation; 5, 7 and 11 refer to APC/C subunits. APC11 is the functional ubiquitin ligase. P, phosphorylated residues.