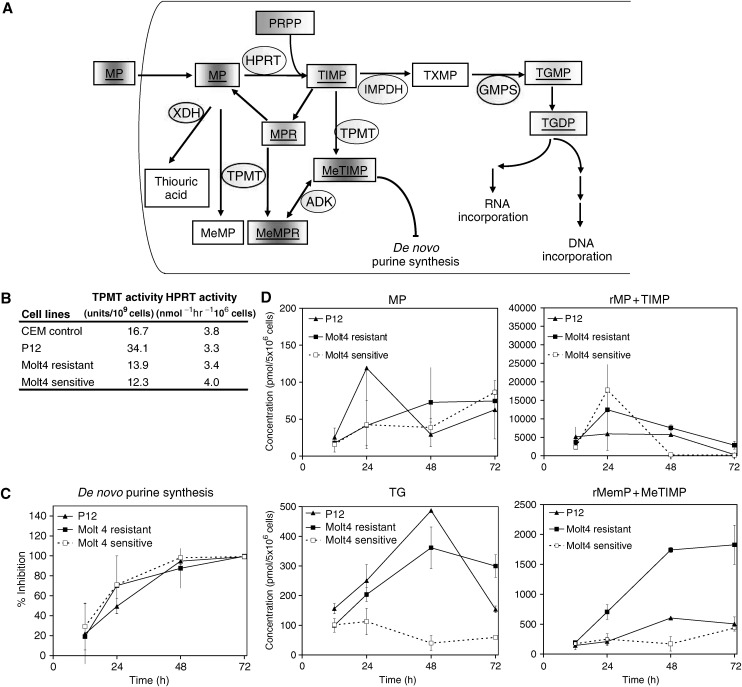
Figure 1.
(A) Mercaptopurine metabolic pathway. Intracellular mercaptopurine (MP) is converted into thioinosine monophosphate (TIMP) by hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT), using 5-phospho-D-ribose-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP). TIMP is converted into thioxanthosine monophosphate (TXMP), then to thioguanosine monophosphate (TGMP), by inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) and guanine monophosphate synthetase (GMPS). TGMP can be converted into thioguanine nucleotide diphosphate (TGDP) and triphosphate (TGTP). Cytotoxic effects occur when TGN is incorporated into DNA or RNA or when methylthioinosine monophosphate (MeTIMP) inhibits de novo purine synthesis. The inactivation of MP is catalysed by xanthine oxidase (XDH), thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) or adenosine kinase (ADK). Alternative products are mercaptopurine riboside (rMP), methylmercaptopurine (MeMP), methylmercaptopurine riboside (rMeMP). Enzymes are shown in circles and metabolites in boxes, underlined are metabolites detected in our assay. (B) TPMT and HPRT activity are listed for the three cell lines. (C) DNPS inhibition following MP treatment was measured in three cell lines at the sampling hours indicated. (D) Shows intracellular MP metabolite concentration in the three cell lines P12 resistant, Molt-4 resistant, and Molt-4 sensitive at the sampling hours indicated. Measured were MP, rMP+TIMP, all thioguanine nucleotides (TG), rMeMP+MeTIMP.