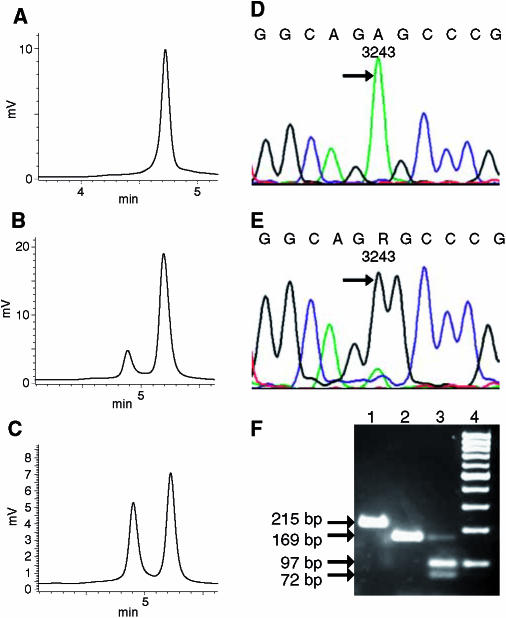
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial DNA analysis of the renal carcinoma with the somatic A3243G mutation. Denaturating HPLC analysis of a PCR fragment (3079–3505) of case 4 at 58°C oven temperature (A–C). The kidney tissue shows a single homoplasmic peak (A), the corresponding renal carcinoma tissue a heteroplasmy over 90% (B) and the mixture of denaturated and reannealed PCR product of kidney and the corresponding tumour tissue resulted in one hetero- and homoduplex peak of the similar height (C). Sequence analysis of the PCR product indicated the wild-type 3243A variant in the unaffected kidney tissue (D), and the 3243G mutation in the corresponding carcinoma tissue (E), as indicated by arrows. Agarose gel analysis of a restriction digestion of a PCR fragment (3118–3332) with HaeIII, which specifically recognizes the 3243G mutation, and two control sites within the PCR fragment yielding two small fragments (F): undigested full-length PCR fragment of 215 base pairs (lane 1); kidney tissue resulting in a 169-base pair fragment (lane 2); carcinoma tissue resulting in a weak 169-base pair fragment of the residual wild-type 3243A variant as well as 72- and 97-base pair fragments, indicating the 3243G mutation (lane 3); 100 bp molecular weight marker (lane 4). R=G+A.