Figure 3.
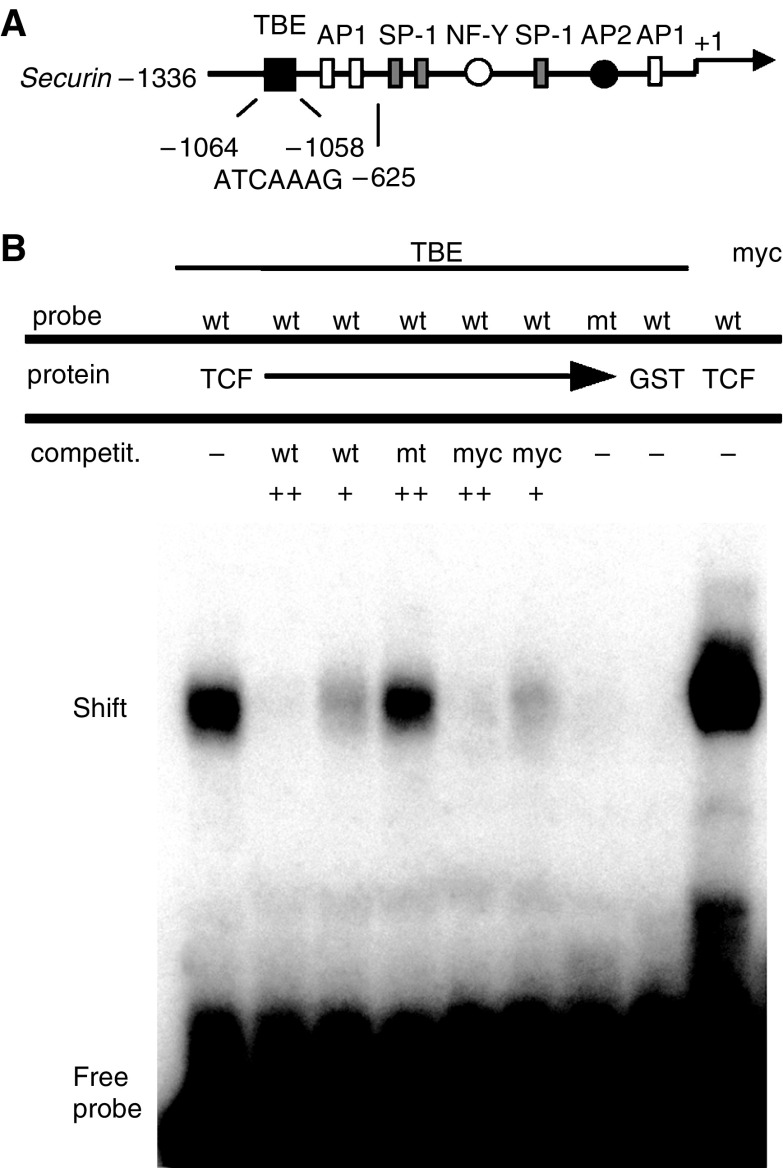
Identification of a TCF-binding element in the human securin promoter. Structure of the human securin promoter (A). The TBE motif is shown as a closed box and the corresponding nucleotide sequence as well as the location relative to the transcription initiation site is indicated below (not drawn to scale). Known transcription factor binding sites are shown (Kakar, 1999; Clem et al, 2003). Electromobility shift assay shows specific interaction of recombinant TCF-4 DNA-binding domain (TCF) with oligonucleotides containing the wild-type TBE motif (TBE, wt) of the securin promoter by complex formation (B, shift). Oligonucleotides were used as labelled probes and as unlabelled competitors (competit.) in two different amounts (wt, wild type; mt, mutant; myc, TBEs of the c-myc promoter as positive control). Competition of wild-type securin TBE and c-myc TBE, but not mutant TBE, indicates specific TCF-4 protein binding. The wild-type DNA probe does not bind to GST protein alone nor does TCF bind to mutant TBE (B).