FIGURE 4. The Sbh1p or Sbh2p-TM domains are sufficient to rescue loss of Sbh1p and Sbh2p.
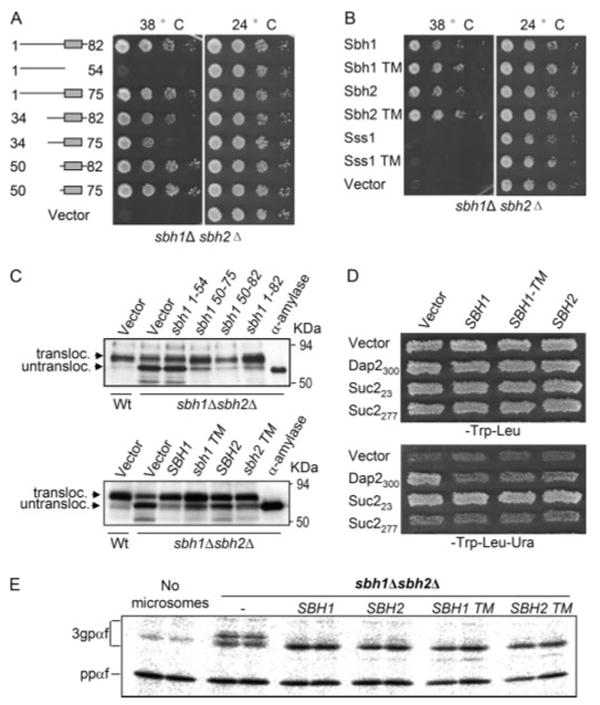
A, multicopy suppression of temperature sensitivity of sbh1Δ sbh2Δ cells by different mutant forms of SBH1. sbh1Δ sbh2Δ cells were transformed with SBH1 wild type or the indicated mutants expressed from the ADH1 promoter in the 2μ vector pVT102U and the growth of the cells was monitored at 38 and 24 °C. B, the Sbh1p-TM or Sbh2p-TM but not the Sss1p-TM domain rescues temperature sensitivity of sbh1Δ sbh2Δ cells. sbh1Δ sbh2Δ cells transformed with plasmids expressing either the full-length (FL) or only the TM domain (TM) of Sbh1p, Sbh2p, or Sss1p were replica plated to 38 and 24 °C and then rescued by the Sbh1p-or Sbh2p-TM domains. C, wild type cells (H3384) and sbh1Δ sbh2Δ (H3388) cells expressing bacterial α-amylase were transformed with plasmids YEpSBH1-(1–54), YEpSBH1-(50–75), YEpSBH1-(50–82), YEpSBH1-(1–82) or the empty vector (upper panel) or with plasmids YEpSBH1-(1–82), YEpSBH1-(50–75), YEpSBH2-(1–88), YEpSBH2-(57–82), or empty vector (lower panel), and the intracellular α-amylase was analyzed in cell lysates by Western blotting with antibodies to α-amylase. α-Amylase indicates the lane loaded with purified bacterial α-amylase. D, UTA translocation assay on sbh1Δ sbh2Δ cells. Strain H3543 was transformed with plasmids encoding reporter proteins Suc223, Sec2277, Dap2300, or the empty vector pRS314 and either the empty plasmid or plasmids encoding Sbh1p, Sbh1p-TM domain, or Sbh2p. The growth of patches of these transformants was tested on SCD-Trp-Leu or on SCD-Trp-Leu-Ura plates to score for translocation of the Ura3p containing reporters. E, the Sbh1p and Sbh2p-TM domains rescue the in vitro glycosylation defect in sbh1Δ sbh2Δ cells. Microsomes prepared from H3232 cells transformed with YEpSBH-(1–82), YEpSBH1 (50–75), YEpSBH2-(1– 88), YEpSBH2-(57– 82), or the empty vector pVT102U were assayed for in vitro translocation of ppαf and mobility of translocation products.
