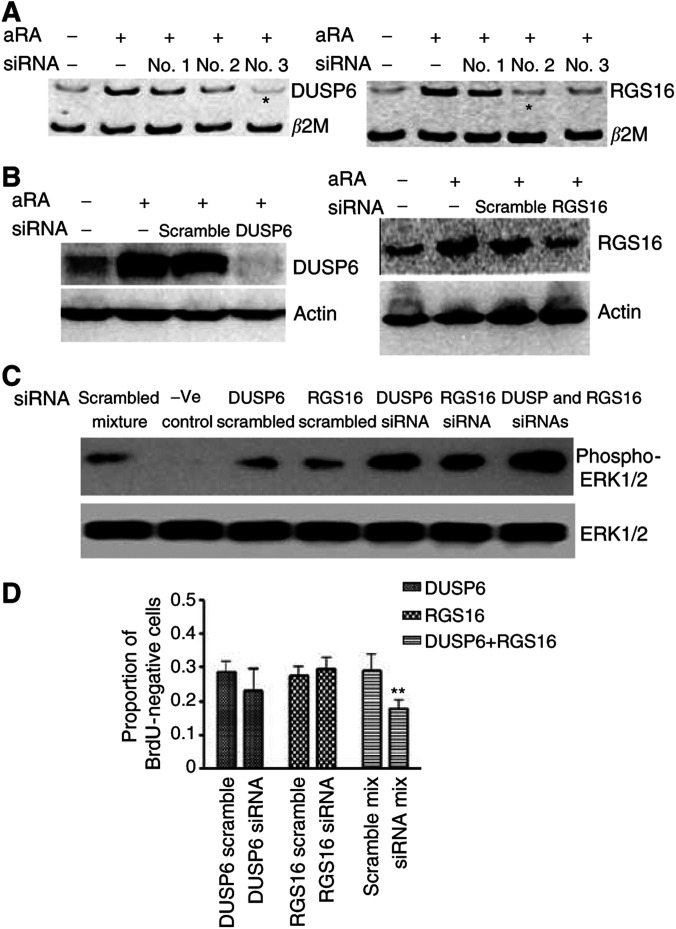
Figure 4.
Synchronous expression of both DUSP6 and RGS16 contributed to RA-induced growth inhibition. (A) DUSP6 and RGS16 gene expression was analysed with competitive RT–PCR with the housekeeping gene β2M as an internal control with samples from SH-SY5Y cells transfected with DUSP6 or RGS16 siRNA or scrambled siRNA and treated with 10 μM aRA for 48 h. *Indicates the siRNAs of choice for protein and functional studies. (B) DUSP6 and RGS16 protein was analysed by Western blot with samples from SH-SY5Y cells transfected with scrambled siRNA, DUSP6, or RGS16 siRNA and treated with 10 μM aRA or control solvent for 48 h. β-Actin protein was used as a loading control. (C) Phosphorylated ERK1/2 was analysed by Western blot with samples from SH-SY5Y cells transfected with scrambled, DUSP6, RGS16 siRNA, or siRNA combinations and treated with 10 μM aRA for 60 h. Total ERK1/2 protein was used as a loading control. (D) BrdU incorporation into proliferating cells was analysed in SH-SY5Y cells after transfection with scrambled or target gene siRNAs plus treatment with 10 μM aRA for 64 h. BrdU-positive cells treated with vehicle solvent and transfected with scrambled siRNA were artificially set as 100%. Error bar represented standard error. **Indicated statistical significant difference (P<0.05).