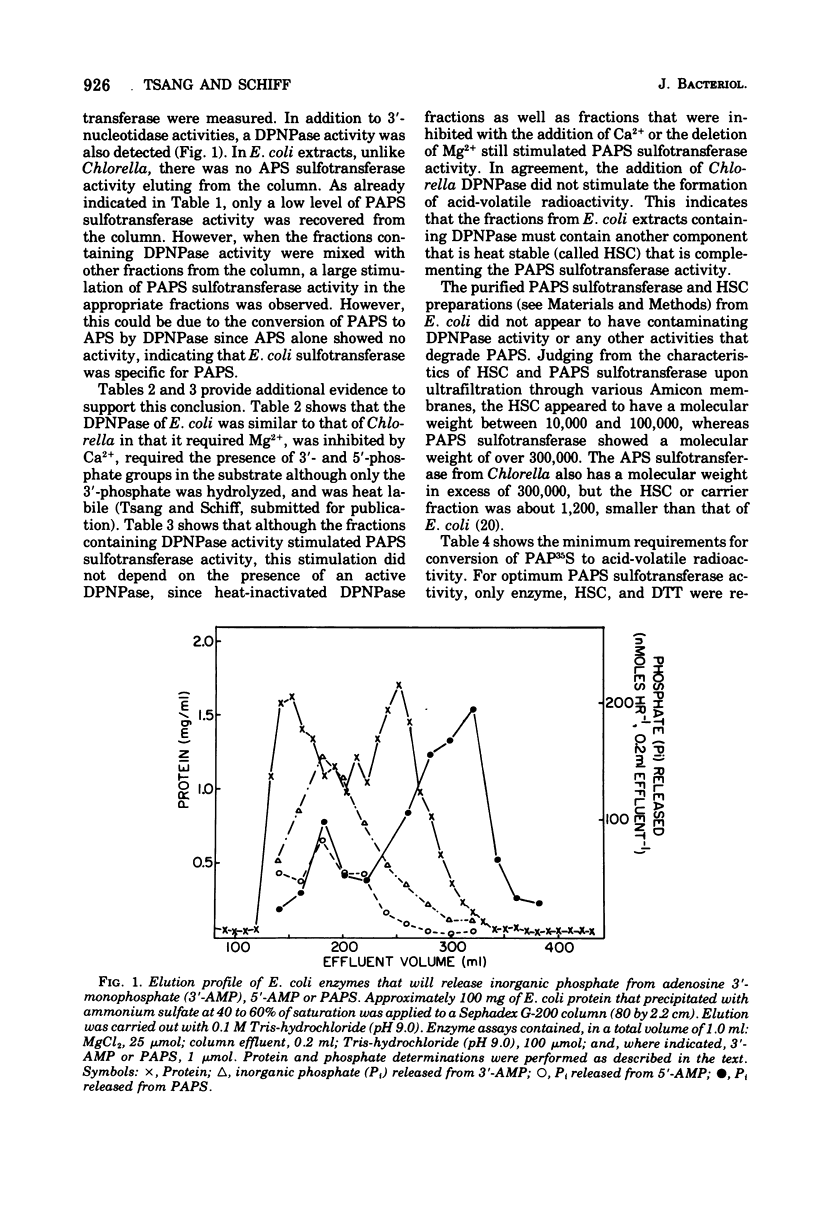
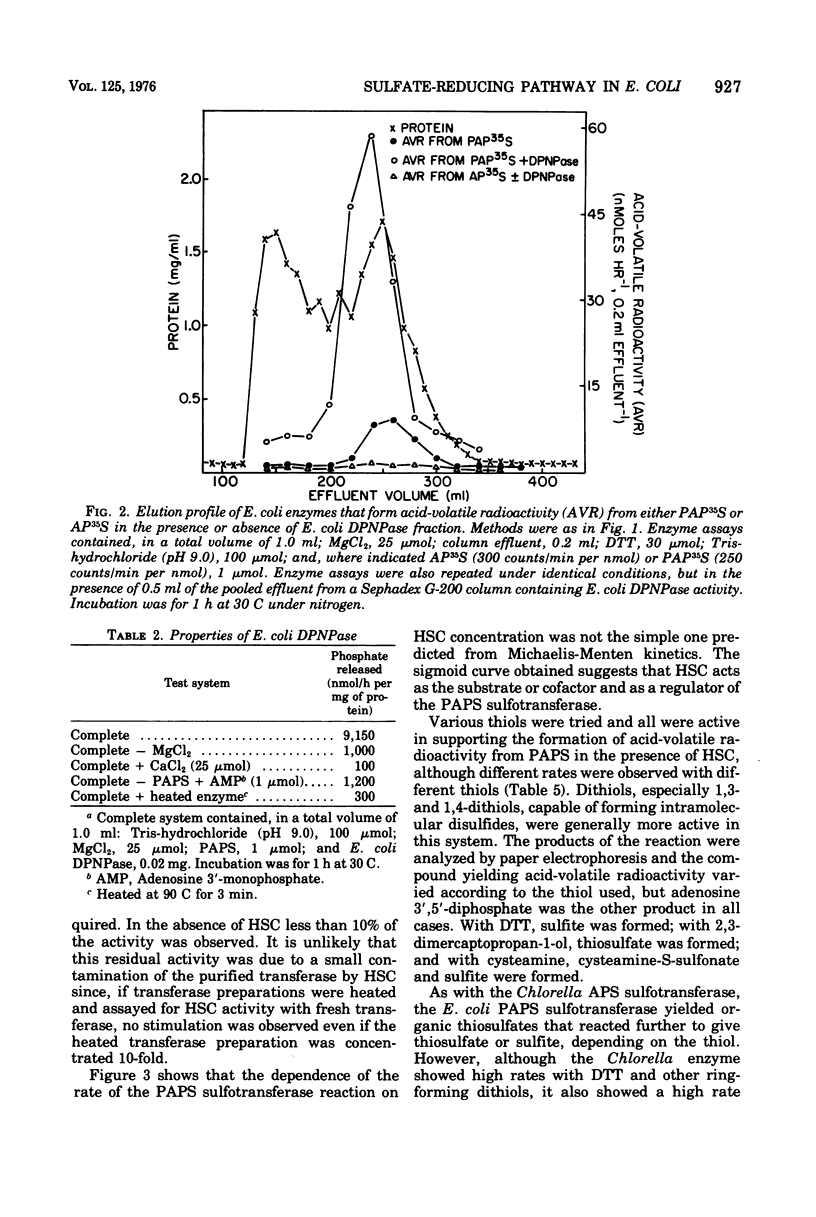
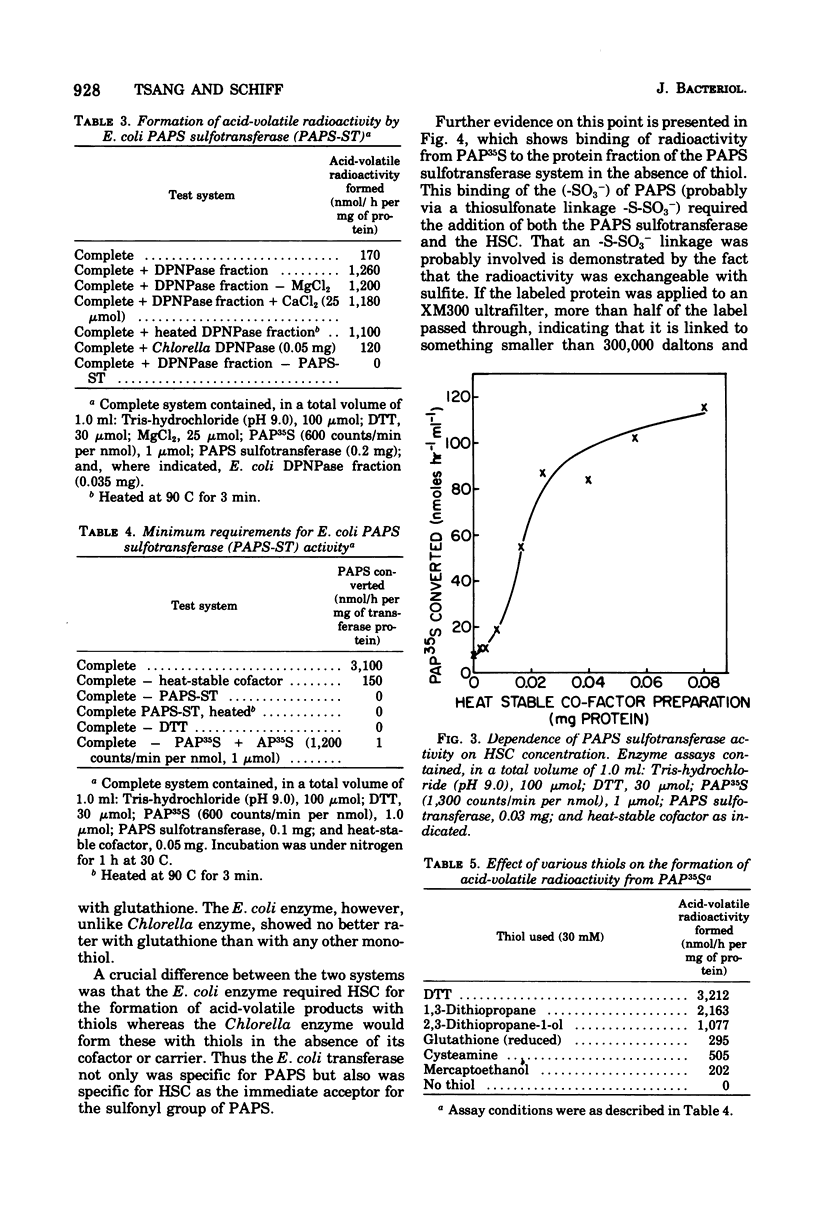
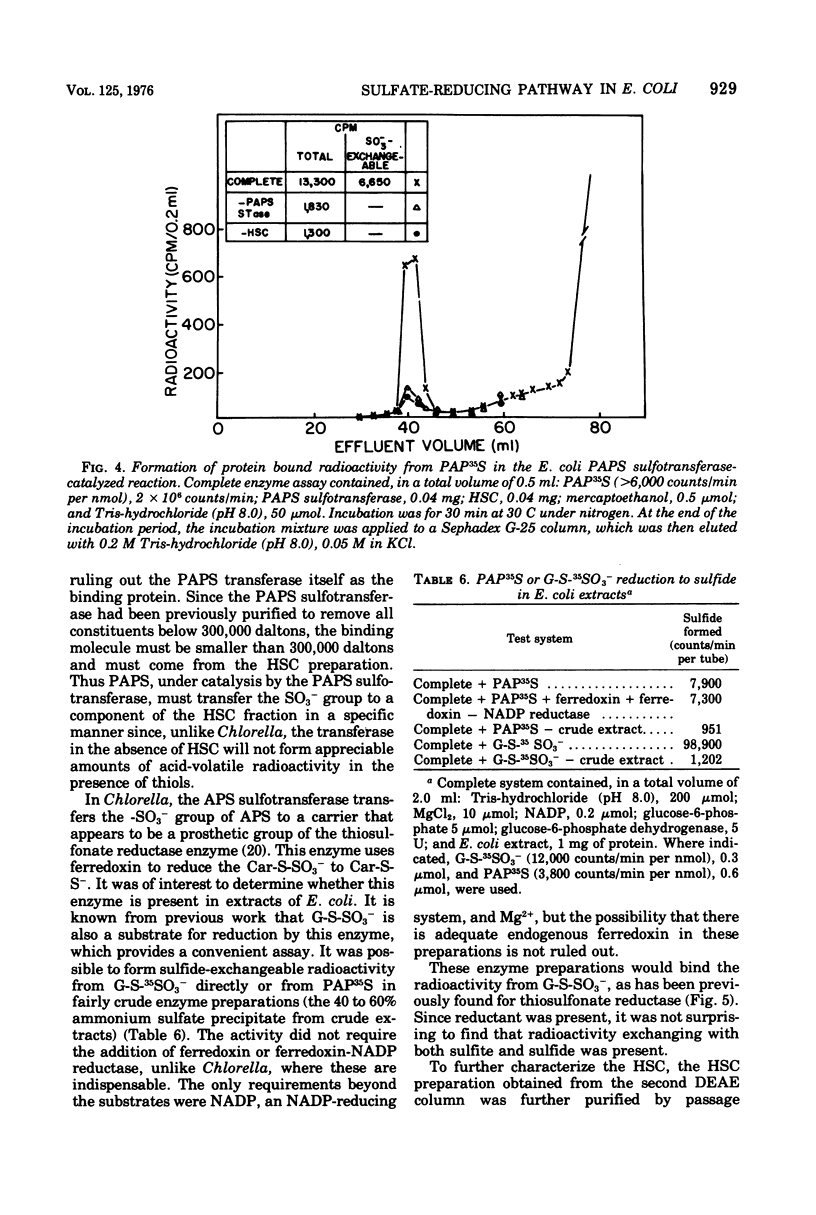
Abstract
Although a sulfate-reducing pathway in Escherichia coli involving free sulfite and sulfide has been suggested, it is shown that, as in Chlorella, a pathway involving bound intermediates is also present. E. coli extracts contained a sulfotransferase that transferred the sulfonyl group from a nucleosidephosphosulfate to an acceptor to form an organic thiosulfate. This enzyme was specific for adenosine 3'-phosphate 5'-phosphosulfate, did not utilize adenine 5'-phosphosulfate, and transferred to a carrier molecule that was identical with thioredoxin in molecular weight and amino acid composition. In the absence of thioredoxin, only very low levels of the transfer of the sulfo group to thiols was observed. As in Chlorella, thiosulfonate reductase activity that reduced glutathione-S-SO3- to bound sulfide could be detected. In E. coli, this enzyme used reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and Mg2+, but did not require the addition of ferredoxin or ferredoxin nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reductase. Although in Chlorella the thiosulfonate reductase appears to be a different enzyme from the sulfite reductase, the E. coli thiosulfonate reductase and sulfite reductase may be activities of the same enzyme.
Full text
PDF


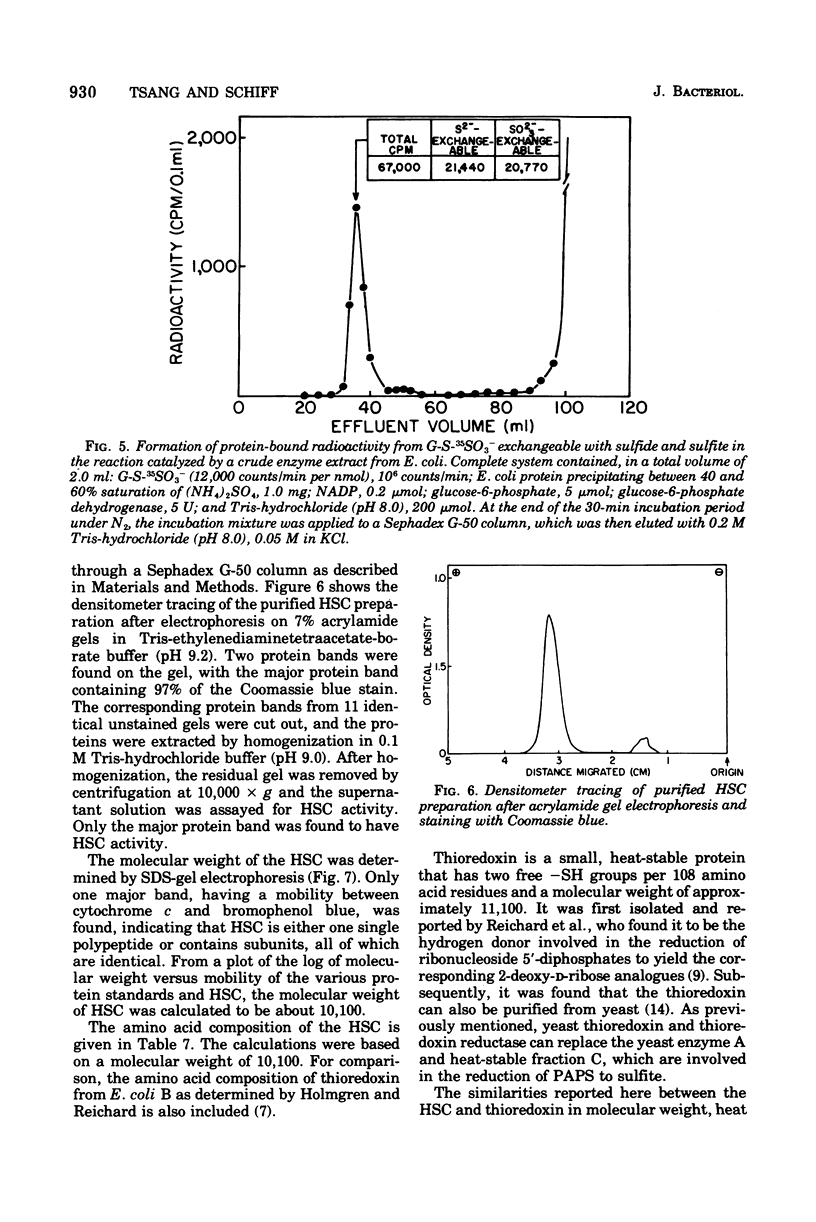
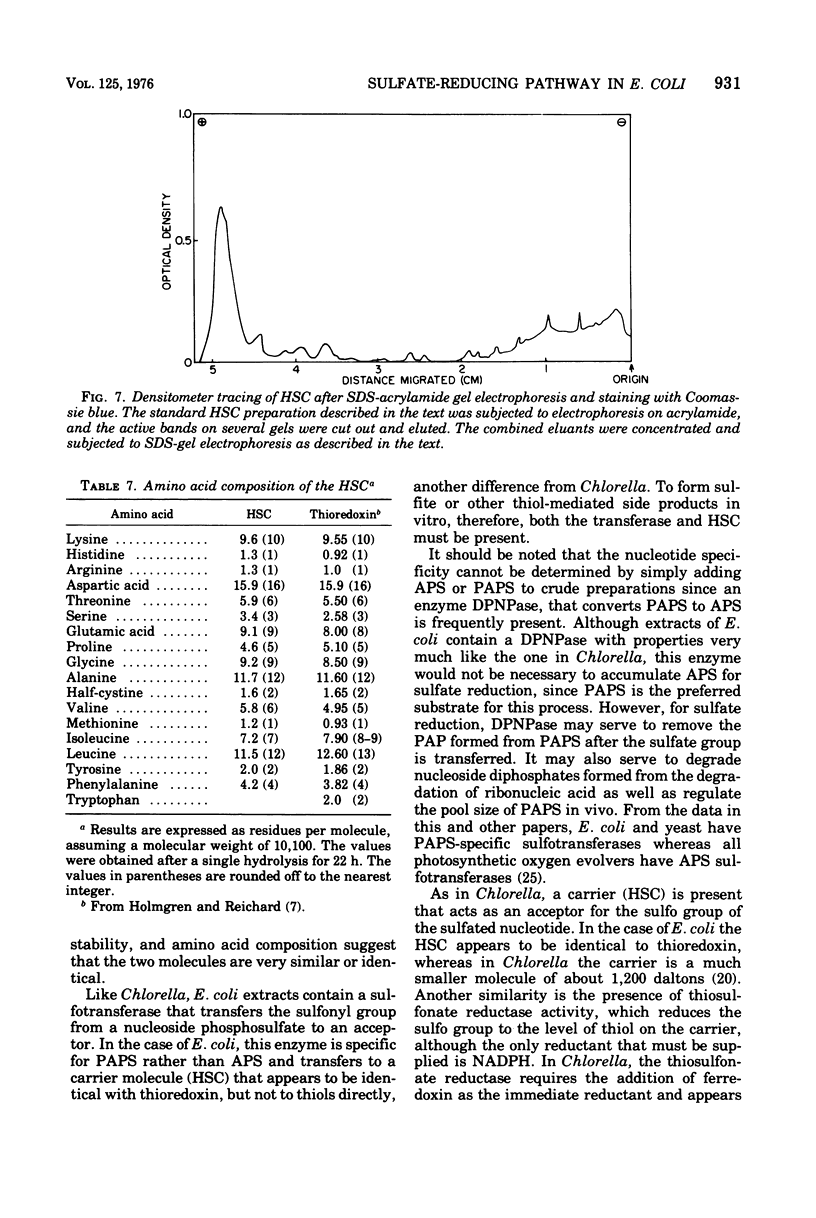
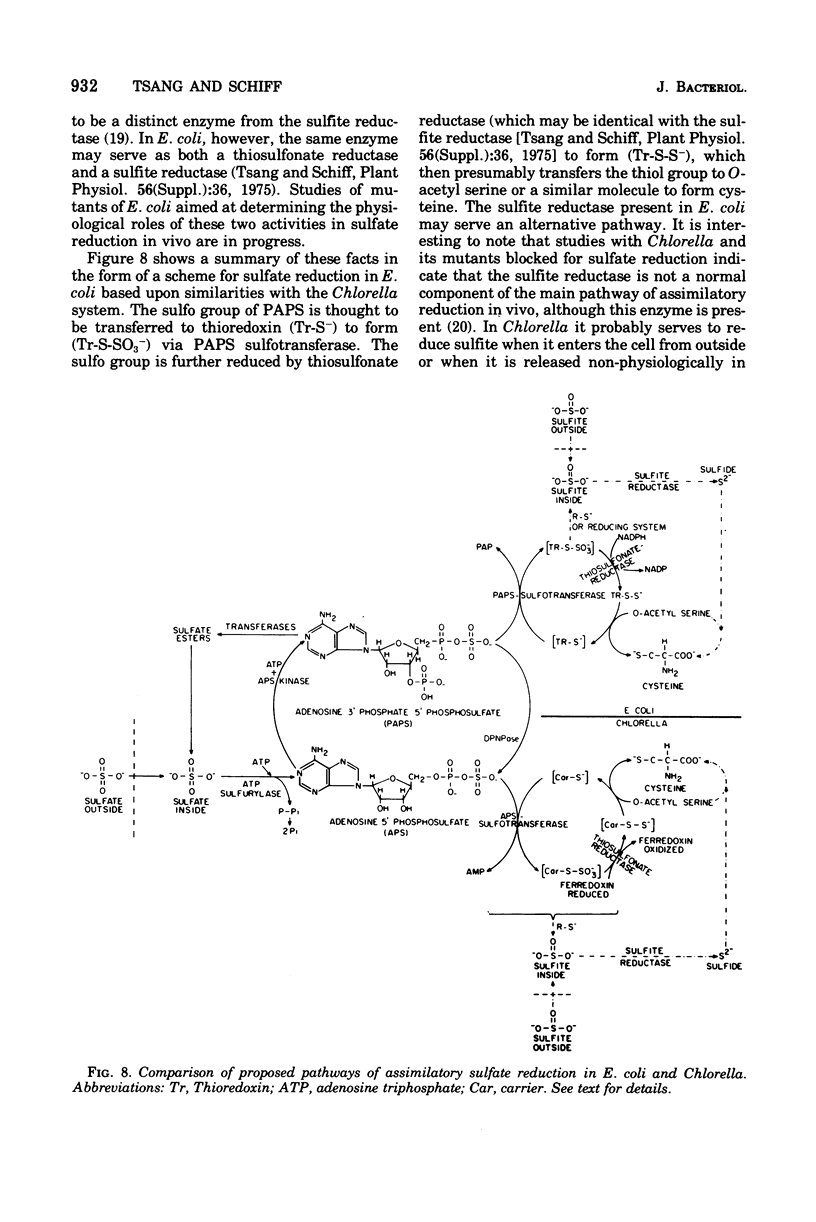

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams W. R., Schiff J. A. Studies of sulfate utilization by algae. II. An enzyme-bound intermediate in the reduction of adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (APS) by cell-free extracts of wild-type Chlorella and mutants blocked for sulfate reduction. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 4;94(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolle A., Epstein R. H., Salser W., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage T4 development: synthesis and relative stability of early and late RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):325–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJIMOTO D., ISHIMOTO M. Sulfate reduction in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1961 Dec;50:533–537. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Porqué P., Baldesten A., Reichard P. Purification of a thioredoxin system from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2363–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Porqué P., Baldesten A., Reichard P. The involvement of the thioredoxin system in the reduction of methionine sulfoxide and sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2371–2374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodson R. C., Schiff J. A. Preparation of adenosine-3'-phosphate-51-phosphosulfate (PAPS): an improved enzymatic method using Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Reichard P. Thioredoxin 2: cleavage with cyanogen bromide. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Sep;2(2):187–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Mortimer M. C. Positive control of sulphate reduction in Escherichia coli. Isolation, characterization and mapping oc cysteineless mutants of E. coli K12. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):589–595. doi: 10.1042/bj1100589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENT T. C., MOORE E. C., REICHARD P. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEOTIDES. IV. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THIOREDOXIN, THE HYDROGEN DONOR FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI B. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3436–3444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J. A TPNH-linked reductase and its relation to hydroxylamine reductase in Enterobacteriaceae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 15;41:553–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASTERNAK C. A., ELLIS R. J., JONES-MORTIMER M. C., CRICHTON C. E. THE CONTROL OF SULPHATE REDUCTION IN BACTERIA. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:270–275. doi: 10.1042/bj0960270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr Enzymatic basis for assimilatory and dissimilatory sulfate reduction. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:933–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.933-939.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUSTER L., KAPLAN N. O. A specific b nucleotidase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):535–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. A., Levinthal M. Studies of sulfate utilization by algae. 4. Properties of a cell-free sulfate-reducing system from chlorella. Plant Physiol. 1968 Apr;43(4):547–554. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Abrams W. R., Schiff J. A. Reduction of adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate to cysteine in extracts from Chlorella and mutants blocked for sulfate reduction. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):423–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. On the mechanism of photosynthetic sulfate reduction. An APS-sulfotransferase from Chlorella. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00408084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. Sulfate reduction in a cell-free system of Chlorella. The ferredoxin dependent reduction of a protein-bound intermediate by a thiosulfonate reductase. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Oct 4;93(1):29–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Davis P. S., Kamin H. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. 3. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: catalytic parameters and the sequence of electron flow. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1572–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Davis P. S. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. IV. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: subunit structure and dissociation into hemoprotein and flavoprotein components. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1587–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Murphy M. J., Kamin H. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. I. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: molecular parameters and prosthetic groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):251–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON L. G., ASAHI T., BANDURSKI R. S. Yeast sulfate-reducing system. I. Reduction of sulfate to sulfite. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1822–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



