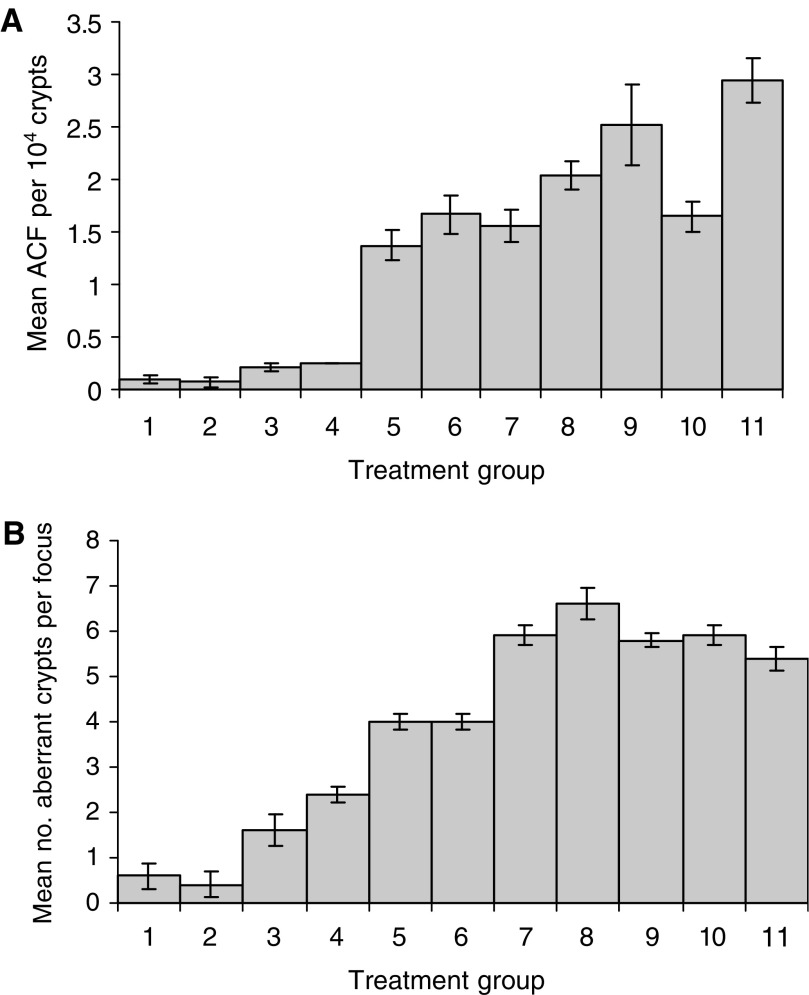
Figure 2.
Treatment effects on ACF. (A) Effects of treatment regimens on ACF number in murine colon. One-way analysis of variance demonstrated significant between-group differences in numbers of ACF per 104 colonic crypts (P<0.001). The Duncan post hoc test identified 5 homogeneous treatment subsets (A–E), showing significant incremental differences in frequency of ACF formation: (A) Groups 1–4, Distilled water, DMSO or λCgN only (1 and 4%); (B) Group 5, MNU alone; (C) Groups 6 and 7, MNU and one 7 day cycle of 1 or 4% λCgN; (D) Group 8, MNU and three 7-day cycles of 1% λCgN; (E) Groups 9 and 11, MNU and either three 7-day cycles of 4% λCgN or continuous 4% λCgN. These subsets showed significant incremental differences of mean ACF per 104 colonic crypts. Group 10 (MNU and 3 × 7-day cycles of 4% λCgN) overlapped subsets C and D. (B) Effects of treatment regimens on size of ACF (crypt multiplicity). One-way analysis of variance demonstrated significant between-group differences in numbers of aberrant crypts per focus {crypt multiplicity} (P<0.01). The Duncan post hoc test identified 5 homogeneous treatment subsets (A–E), showing significant incremental differences in crypt multiplicity: (A) groups 1 and 2, distilled water alone or DMSO alone; (B) groups 3 and 4, continuous treatment with 1 or 4% λCgN alone; (C) groups 5 and 6, MNU alone or MNU and 1 × 7-day cycle of 1% λCgN; (D) groups 9 and 11, MNU and either 3 × 7-day cycles of 4% λCgN or continuous 4% λCgN; (E) group 8, MNU and three 7-day cycles of 1% λCgN. Groups 7 and 10 (MNU and 1 × 7-day cycle of 4% λCgN or continuous 1% λCgN) overlapped subsets D and E.