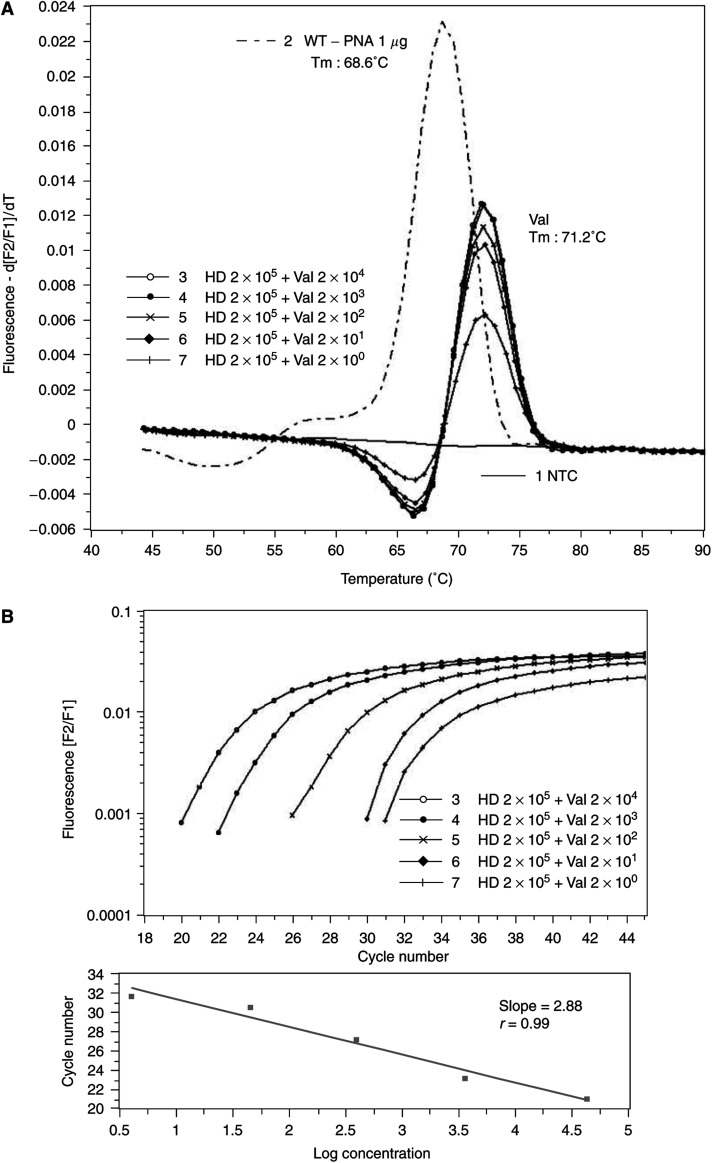
Figure 3.
Titration of assay sensitivity. (A) Sensitivity of melting point analyses using mutant-specific hybridisation probes and wild-type specific PNA. Peripheral blood cells from a healthy donor (HD) and SW 480 colon carcinoma cells, which bear the valine mutation homozygous (Val), were mixed as indicated and DNA was extracted by spin column technology. After rapid cycle amplification of the DNA in the presence of the valine mutation-specific hybridisation probes, the melting curves were analysed by the LightCycler software (version 3.5). Temperature transition rate was 0.3°C s−1. 1: nontemplate control (NTC); 2: WT DNA without PNA; 3: 2 × 104 SW480+2 × 105 WT; 4: 2 × 103 SW480+2 × 105 WT; 5: 2 × 102 SW480+2 × 105 WT; 6: 2 × 101 SW480+2 × 105 WT; 7: 2 × 100 SW480+2 × 105 WT. (B) Quantification of Val DNA in the presence of WT DNA. Serial diluted mixtures of constant amounts of wild-type DNA and varying amounts of Val DNA from cells as indicated (see Figure 3A) were plotted against Ct values (threshold cycle). Slope, r value and regression line are shown. PCR experiments were performed twice.