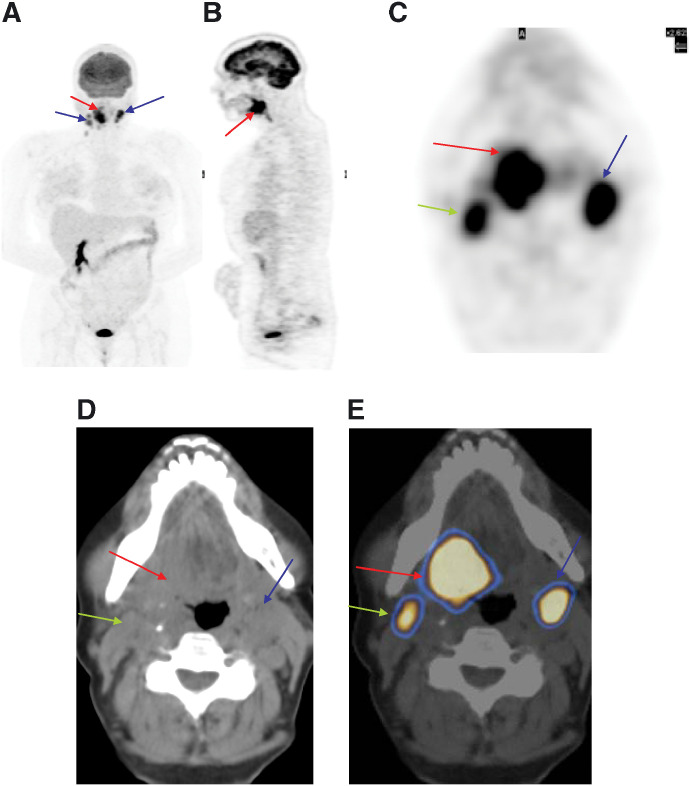
Figure 2.
A 42-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. (A) 18F-FDG PET/CT multiple intensity projection image shows the primary site (red arrow) with bilateral cervical nodes (blue arrows). (B) Sagittal and (C) transaxial images show abnormal uptake in the known primary (posterior part of the tongue) and both cervical regions. (D) CT transaxial section reveals a lesion in the base of the tongue along with left cervical node enlargement. (E) Fused 18F-FDG PET/CT transaxial section at the same level reveals the exact anatomical site of 18F-FDG uptake in the right side of the tongue base extending across the midline and level II left cervical lymph node. The 18F-FDG activity in the right cervical region correlates to the right sternocleidomastoid muscle (green arrow) (a normal variant).