Figure 1.
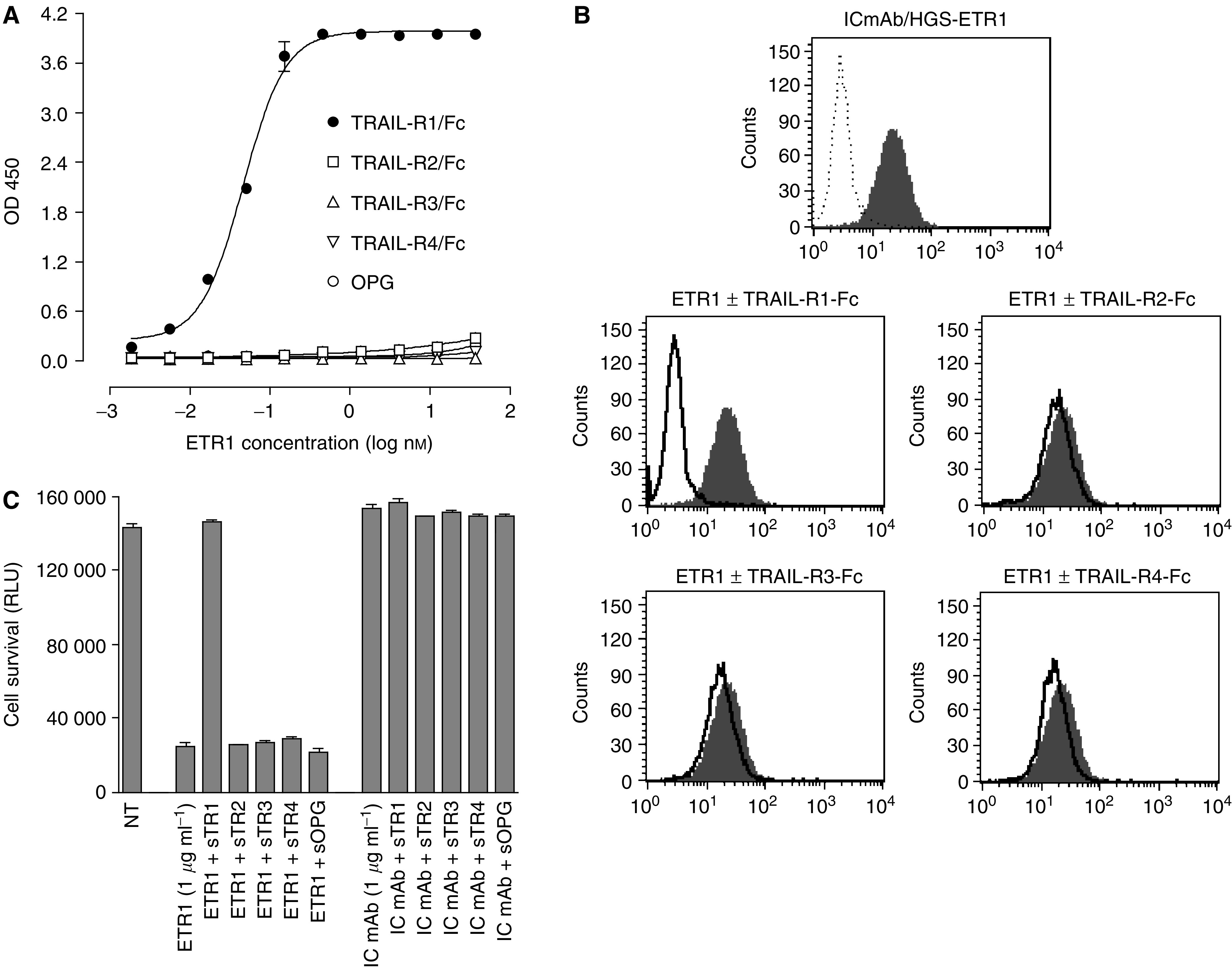
Characterization and specificity of HGS-ETR1 antibody. (A) Direct-binding ELISA data show the binding of indicated concentrations of HGS-ETR1 to the TRAIL-R1 extracellular domain Fc-protein (filled circles) or other TRAIL-R extracellular domain Fc-proteins (open symbols) immobilised on 96-well plates. Binding of HGS-ETR1 to TRAIL-receptors was detected using anti-human Fab-peroxidase conjugate. (B) Binding of HGS-ETR1 to SW480 cells analysed by flow cytometry. The top panel shows the binding of isotype control monoclonal antibody (IC mAb, dotted line) and HGS-ETR1 (shaded peak). The bottom panels show the binding of HGS-ETR1 alone (shaded peak) or binding of HGS-ETR1 in presence of 5 μg ml−1 of the indicated soluble TRAIL-R Fc-protein (solid line). (C) For viability assays, SW480 cells were plated at 1 × 104 cells well−1 in a 96-well plate and cultured overnight. A 1 μg ml−1 concentration of HGS-ETR1 or isotype control monoclonal antibody (IC mAb) was added to the cells in the absence or presence of the indicated soluble TRAIL-receptor proteins (sTRAIL-R1-4, sOPG, 5 μg ml−1) and cell viability, measured as relative light units (RLU), was determined after 48 h. Data is the mean±s.d. of triplicate samples.
