Figure 4. Concentration-dependent block effect of nifedipine on the rat CaV1.2 α1C mutant L-type channels (co-expressed with β2a and α2δ).
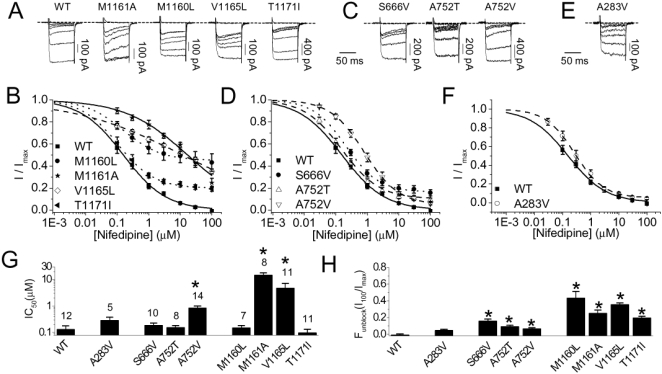
Representatives of barium current records in various nifedipine concentrations (A, C, E) and the mean concentration-effect curves (B, D, F). A & B: the wildtype (WT) and domain III mutants; C. & D: Domain II mutants; and E & F: domain I mutant. The nifedipine concentrations ranged 0, 0.1, 1, 10, 30, 100 µM. The current was elicited by an 80 ms +10 mV depolarizing pulse from a holding potential of −100 mV. In all traces, the baseline was determined by block by 10 µM cadmium (trace with ∼0 pA current). The nifedipine effect was normalized to the unblocked current (Imax) obtained in the absence of the drug. The concentration-effect curves were fit to a modified Hill equation taking into account the possibility of incomplete current block, as described in the methods. The mean concentration-effect curve for the M1161A mutant, known to be important for DHP block[11],[14], serves as a positive control. Summaries of the IC50 values (G), and the residual unblocked current measured at 100 µM nifedipine (H), obtained from the same data presented in Figure B, D, and F. The fraction of current remaining at 100 µM nifedipine (Funblock (I100/Imax)) was used to estimate the completeness of drug block. All the data are presented as mean±s.e.m.; numbers in the parentheses in G reflects the number of independent experiments. * indicates statistical significance relative to the wildtype (p<0.05, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Holm-Sidak).
