Fig. 1.
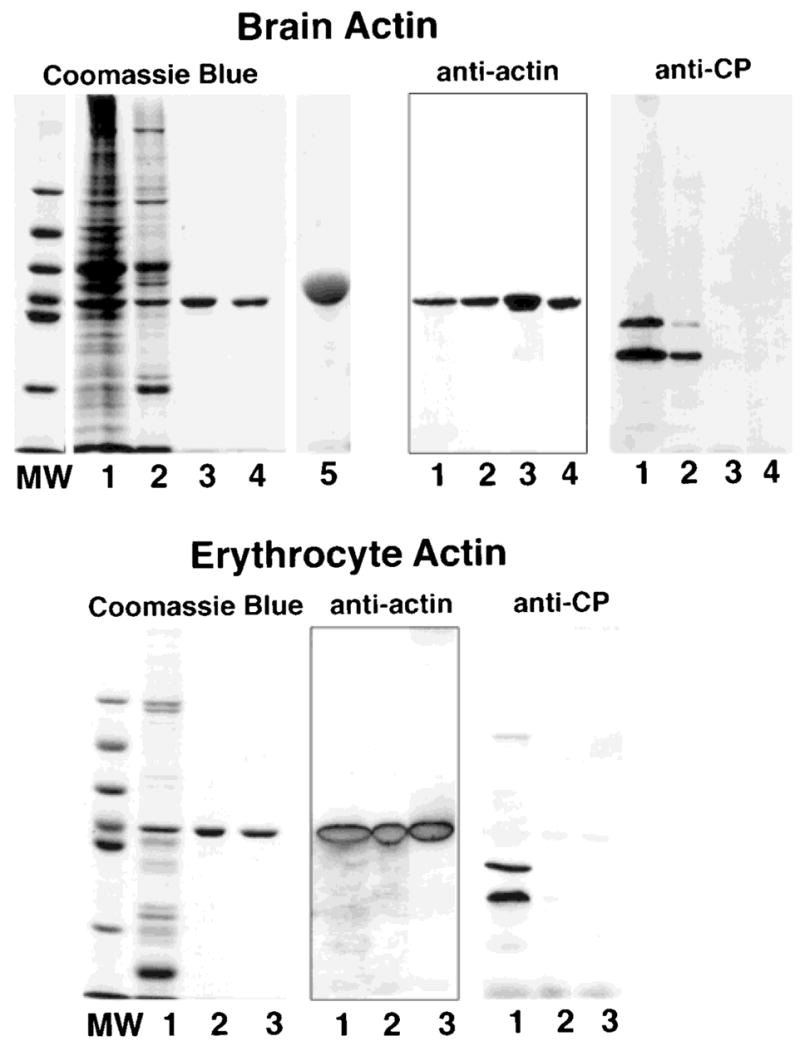
SDS-PAGE and Western blots of actin purified from chicken brain (top) and from bovine erythrocytes (bottom). Samples from each preparation were subjected to SDS-PAGE in 10% gels and stained with Coomassie Blue or transferred to nitrocellulose and probed with mAb C4 to identify actin and with mAbs 5B12 and 3F2 to identify capping protein. Samples from the brain actin preparation: lane 1, brain homogenate after dialysis; lane 2, pool from the DE-53 cellulose column; lane 3, pool from DNase I column; lane 4, pool from a MonoQ column used to concentrate the actin; lane 5, overloaded lane containing 30 μg of brain actin to document the absence of minor contaminants. Samples from the erythrocyte actin preparation: lane 1, pool from the DE-53 cellulose column; lane 2, pool from the DNase I column; lane 3, pool from the MonoQ column. A single band that binds mAb C4 is observed on the purified actin preparation obtained from the DNase I column; the samples are free of capping protein. Lanes labeled MW contain the molecular weight standards with the following molecular weights, from top to bottom: 97 kDa, 66 kDa, 55 kDa, 43 kDa, 40 kDa and, 31 kDa.
