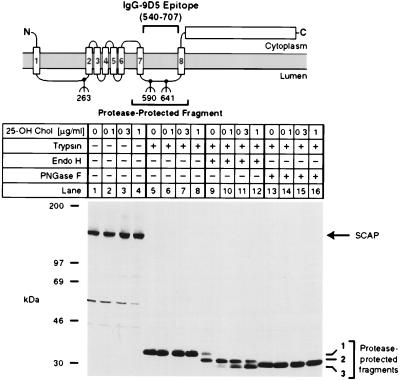
Figure 4.
Sterols alter endo H sensitivity of SCAP. The diagram shows a schematic of the domain structure of SCAP, denoting the approximate position of the protease-resistant fragment recognized by mAb IgG-9D5. Numbers below the diagram denote sites of N-linked glycosylation (5). On day 0, CHO-7 cells were set up in medium A supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum and 50 μg protein/ml of low density lipoprotein. On day 2, cells were switched to medium A containing 10% lipoprotein-deficient serum, 50 μM compactin, 50 μM sodium mevalonate, and 0.1% ethanol containing the indicated final concentration of 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OH Chol.). After incubation for 16 h, cells were harvested, and membrane fractions were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. Aliquots of the membrane fraction (42 μg protein) were incubated in the absence (lanes 1–4) or presence (lanes 5–16) of 17 μg/ml of trypsin. Proteolysis was stopped, and the samples were incubated for 16 h at 37°C in the absence (lanes 1–8) or presence (lanes 9–16) of the indicated glycosidase, subjected to SDS/PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and immunoblotted with 10 μg/ml of IgG-9D5. The filter was exposed to film for 1.5 min. Numbers 1–3 on the right denote differentially glycosylated forms of the protease-resistant SCAP fragment containing either two (band 1), one (band 2), or no (band 3) N-linked oligosaccharides (5).