Figure 2.
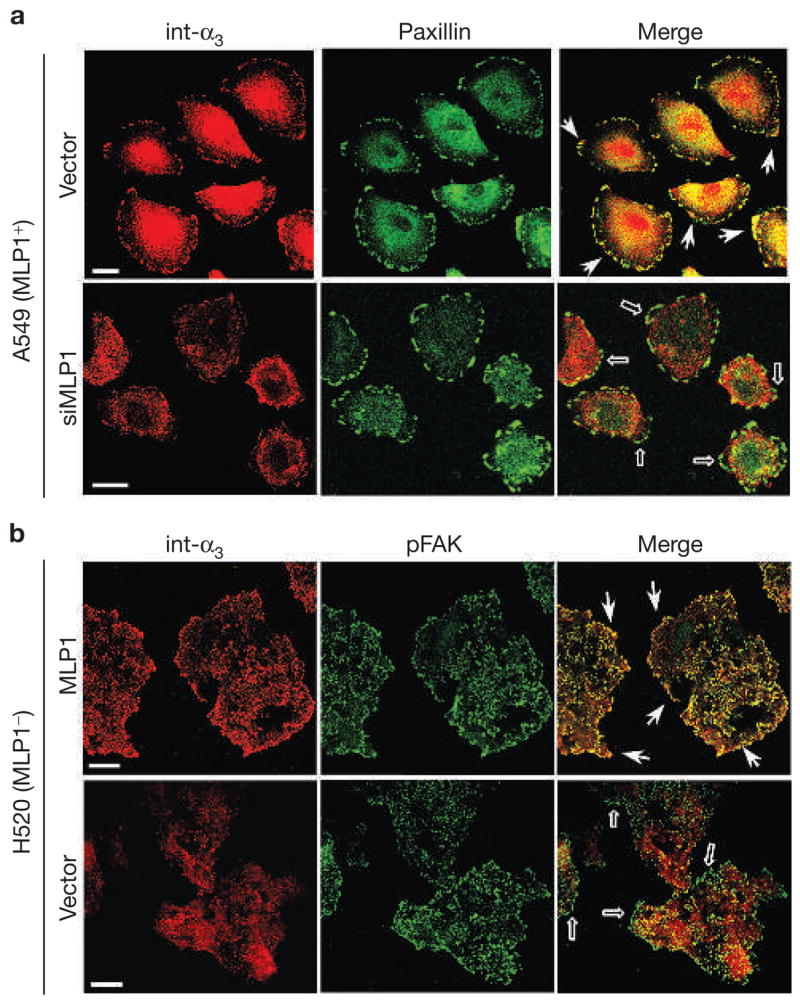
MLP1 is necessary for integrin α3 protein localization to adhesion plaques. (a) A549 cells transfected with empty vector or vector containing MLP1-specific oligonucleotide duplex #1 (siMLP1), as in Fig. 1e, were double-stained for paxillin (green) and integrin α3 (int-α3; red). In vector-transfected cells, integrin α3 colocalized prominently with paxillin in adhesion plaques at the migration front (examples indicated by arrows). In cells transfected with vector expressing MLP1-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA), integrin α3 no longer colocalized with paxillin in the cell periphery (empty arrows). (b) H520 cells were infected with empty adenovector or vector containing the MLP1 coding sequence at the m.o.i. of 10 (as in Fig. 1b), and double-stained for phospho-focal adhesion kinase (pFAK; green) and integrin α3 (red). Each stained area is a cluster of 5–10 cells but the peripheral pFAK appears mostly in cells at the leading edge. Without MLP1, integrin α3 is not colocalized with pFAK at the periphery (empty arrows). Expression of MLP1 results in re-localization of integrin α3 to pFAK-containing plaques at the periphery (arrows). Scale bars, 20 μm.
