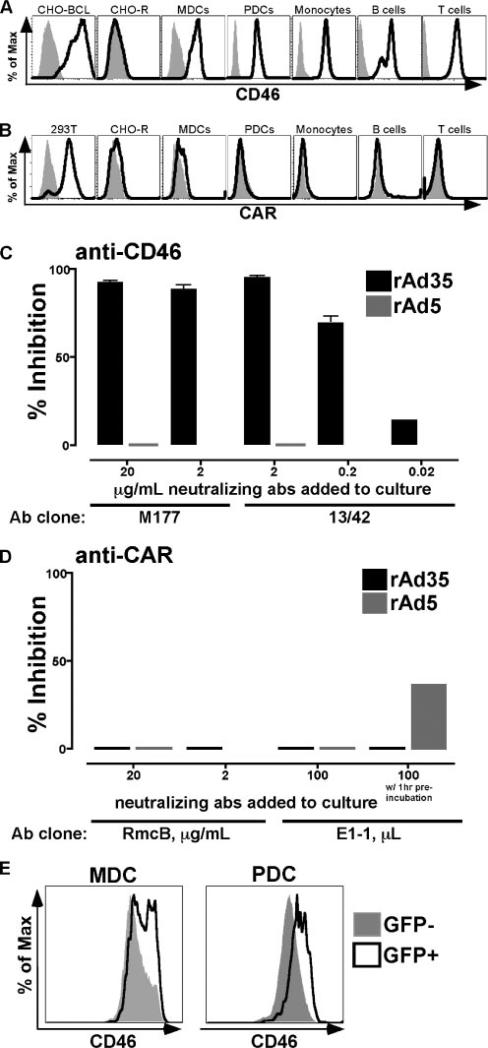
FIGURE 2.
rAd35 uses CD46 for infection while rAd5 may use a CAR independent pathway. A and B, CD46 and CAR expression was assessed on various cell populations. The histograms show stained cells (black lines) vs the unstained control (gray shaded histogram) for each cell type. CHO-BCL and CHO-R cell lines were used for CD46 positive and negative controls, respectively, whereas 293T and CHO-R cell lines were used as the CAR-positive and -negative controls, respectively. Monocytes, MDCs, PDCs, B cells, and T cells expressed CD46 (A), whereas CAR expression (B) was undetectable on these cell types. C and D, MDCs were exposed to either rAd5-GFP or rAd35-GFP for 24 h in the presence and absence of neutralizing anti-CD46 and anti-CAR Ab. Values are the percent inhibition (mean ± SEM) of infection of either rAd5 (gray bars) or rAd35 (black bars). C, Infection of MDCs by rAd35, but not rAd5, was effectively blocked in the presence of either of the two clones of anti-CD46-neutralizing Ab. D, Infection of MDCs by rAd5 and rAd35 was not or poorly blocked in the presence of either of the two neutralizing anti-CAR Ab if anti-CAR and rAd5 exposure occurred simultaneously, whereas preincubation with anti-CAR clone E1-1 showed partial blocking of Ad5 infection. E, CD46 expression was found to be higher on rAd35-infected GFP+ DCs than GFP− DCs within the same culture.